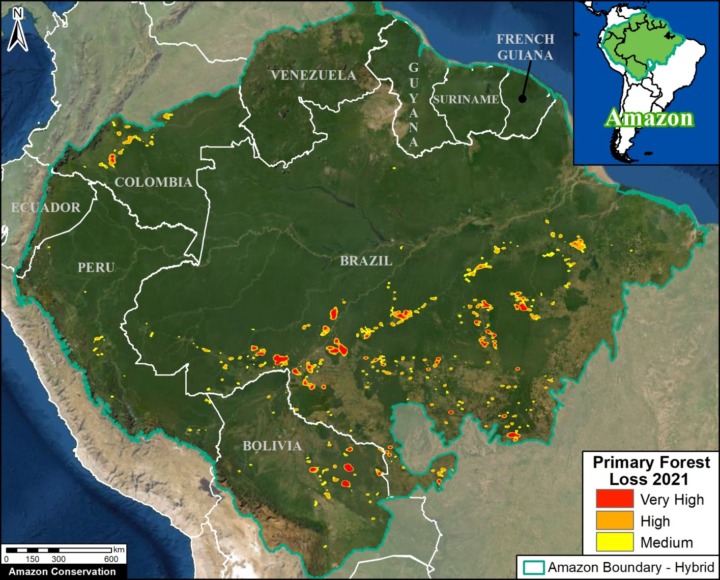
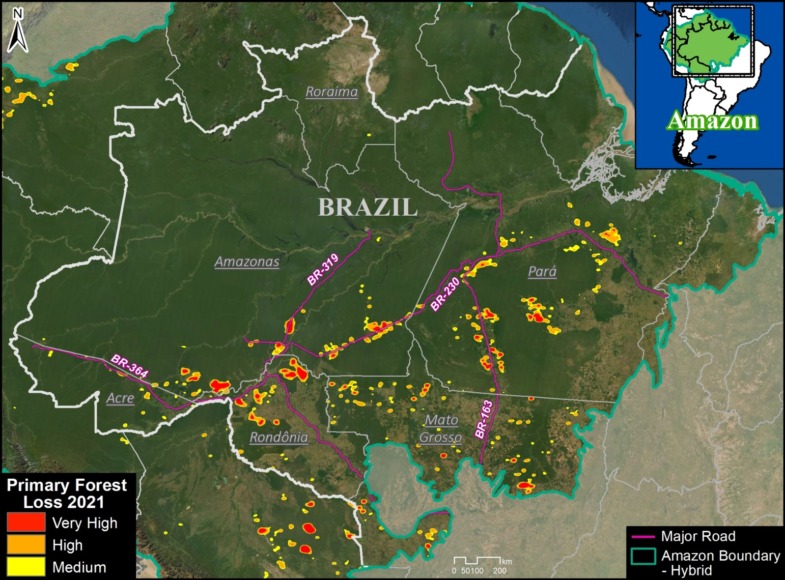
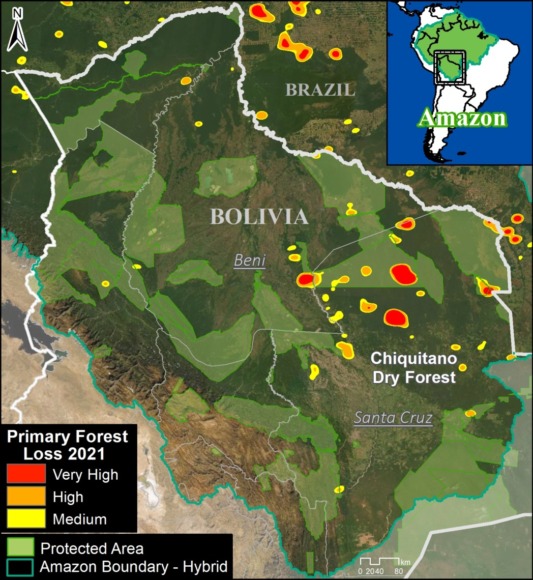
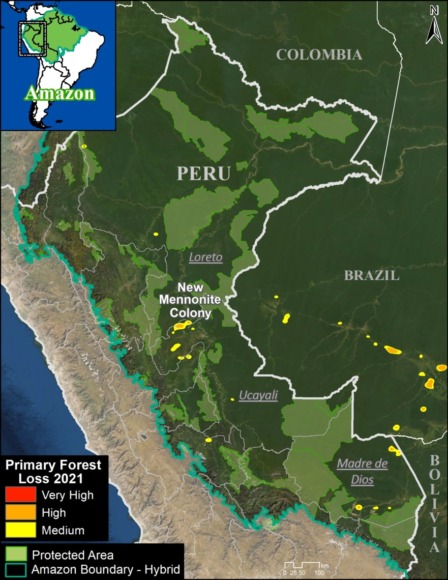
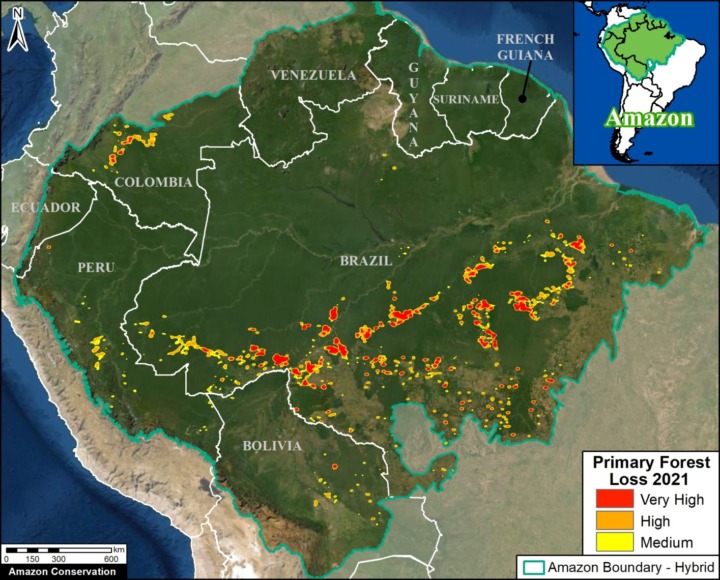
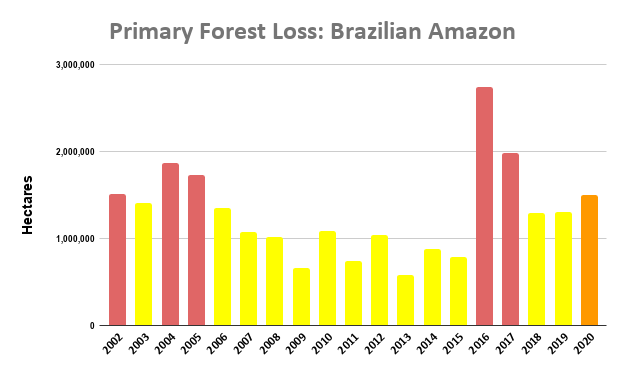
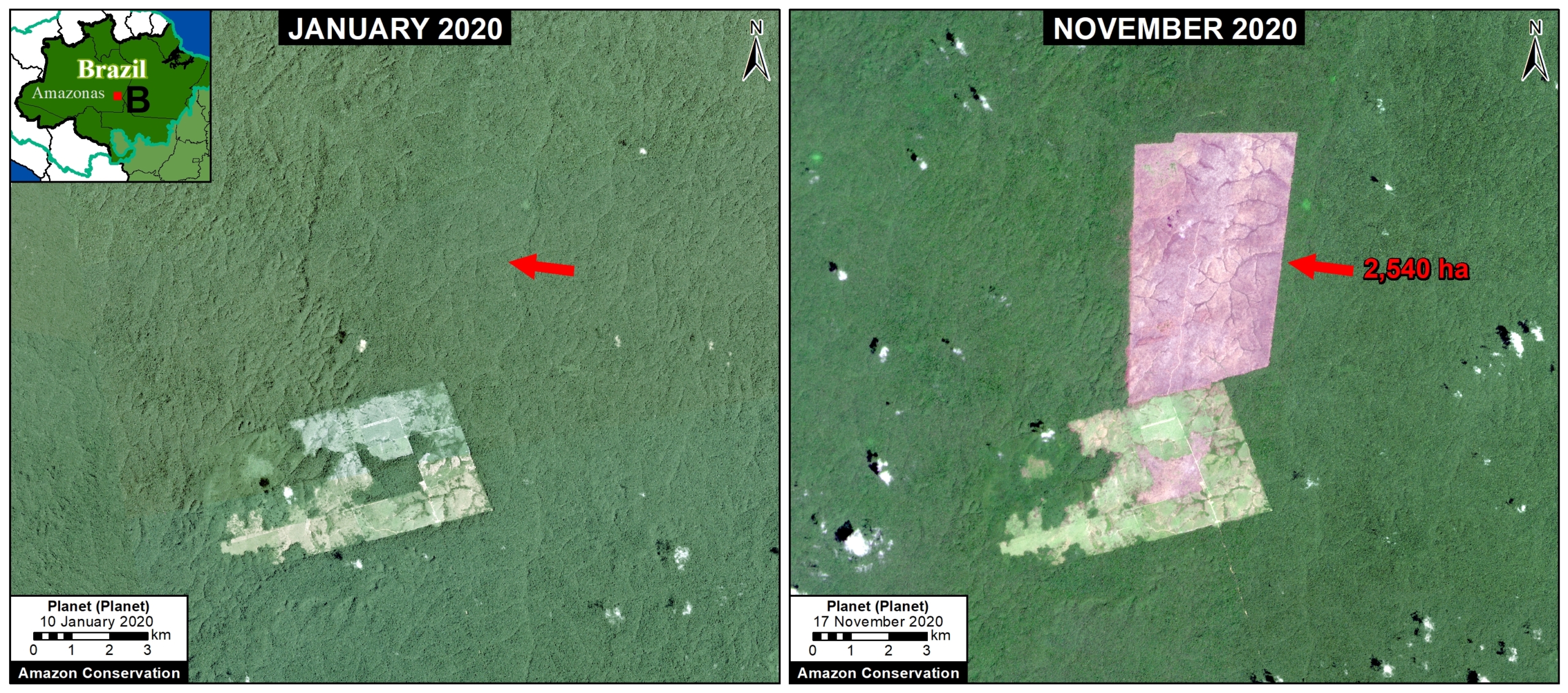
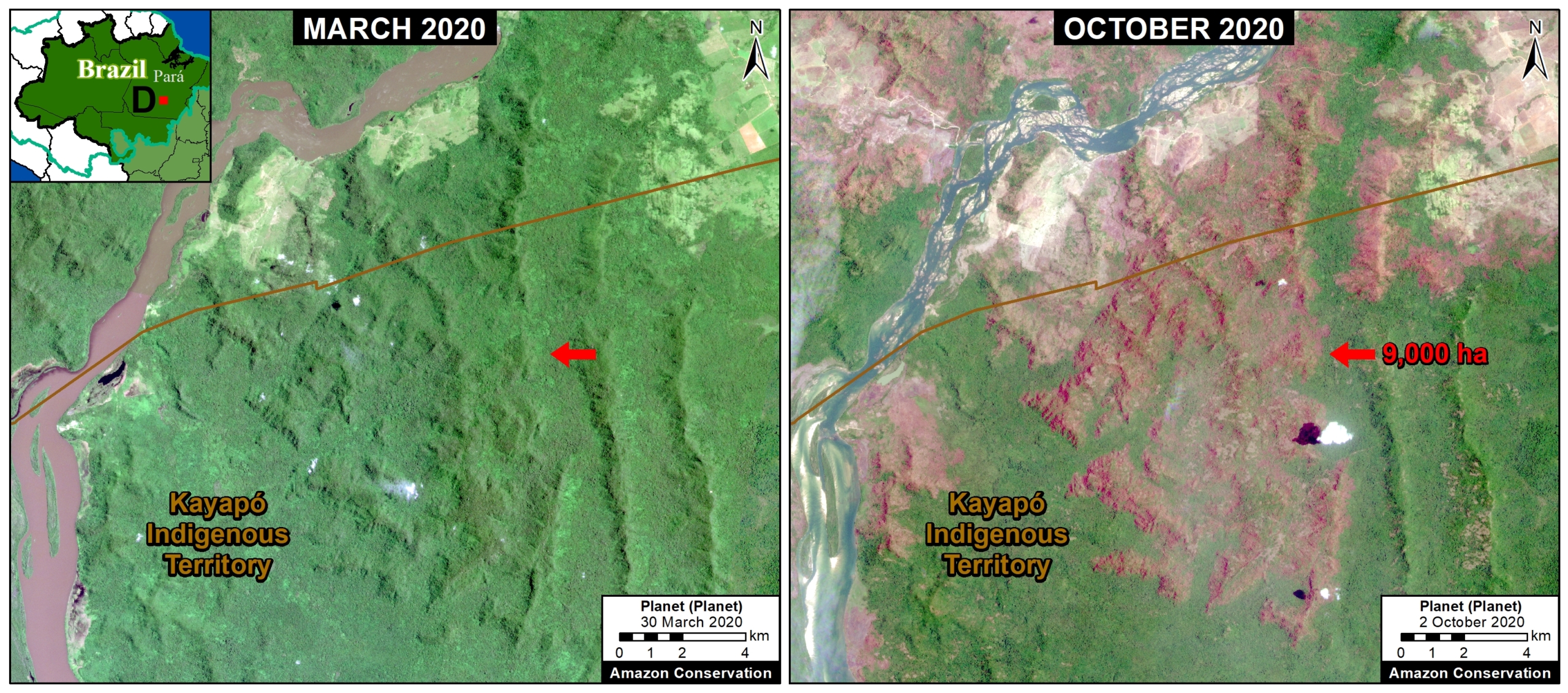
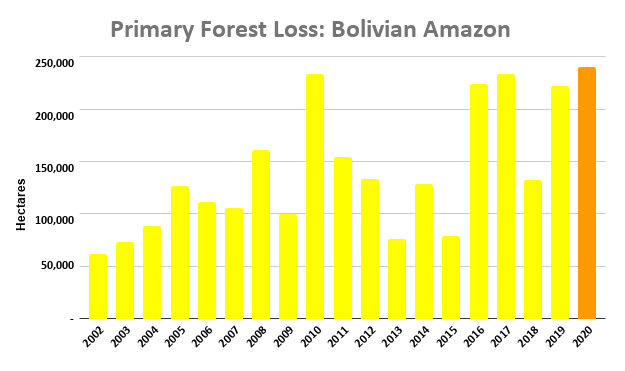
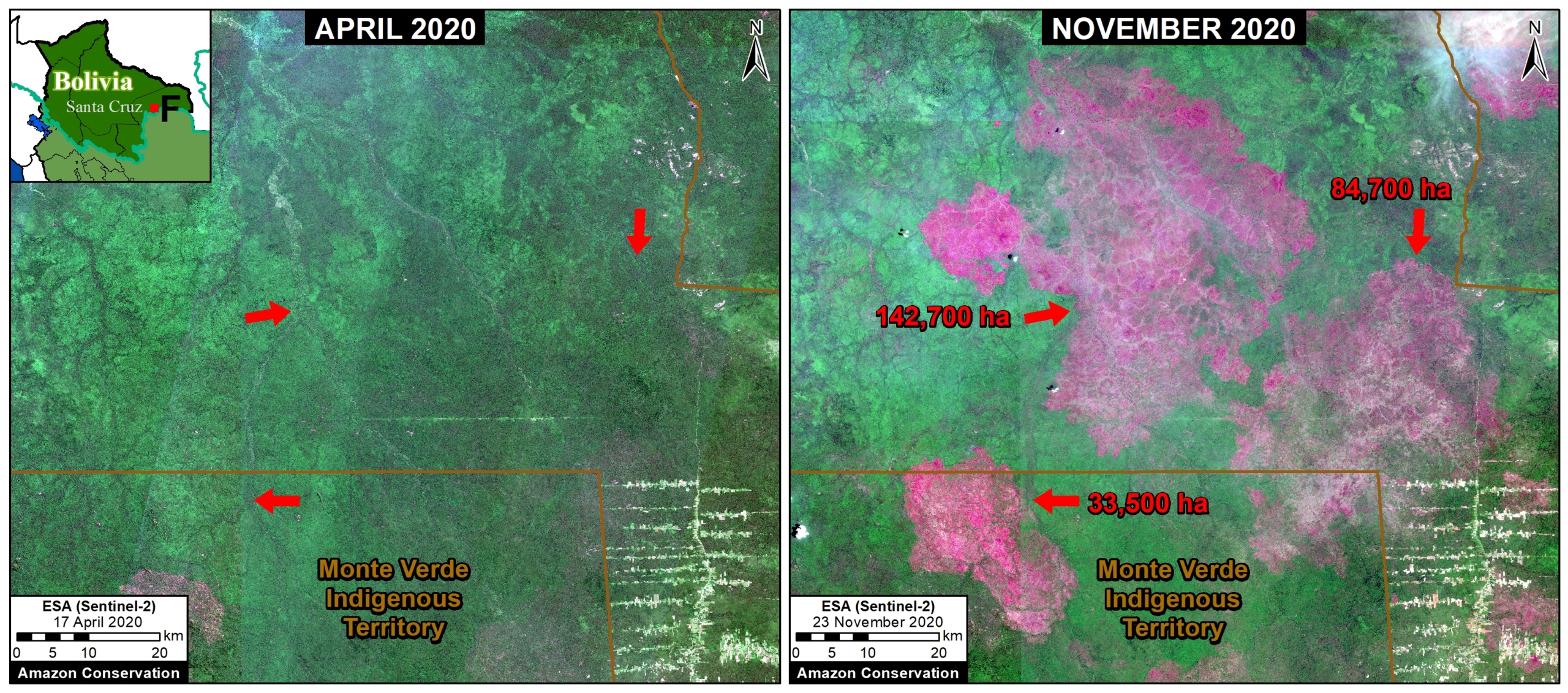
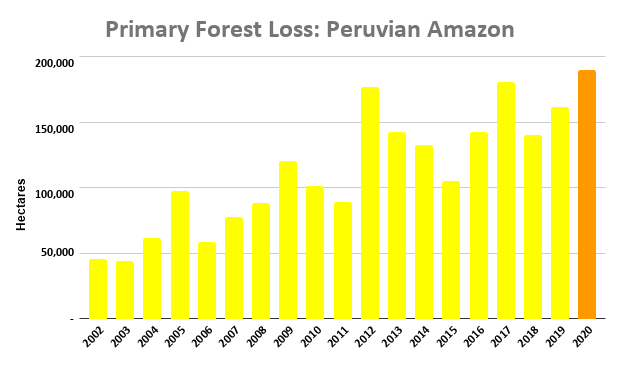
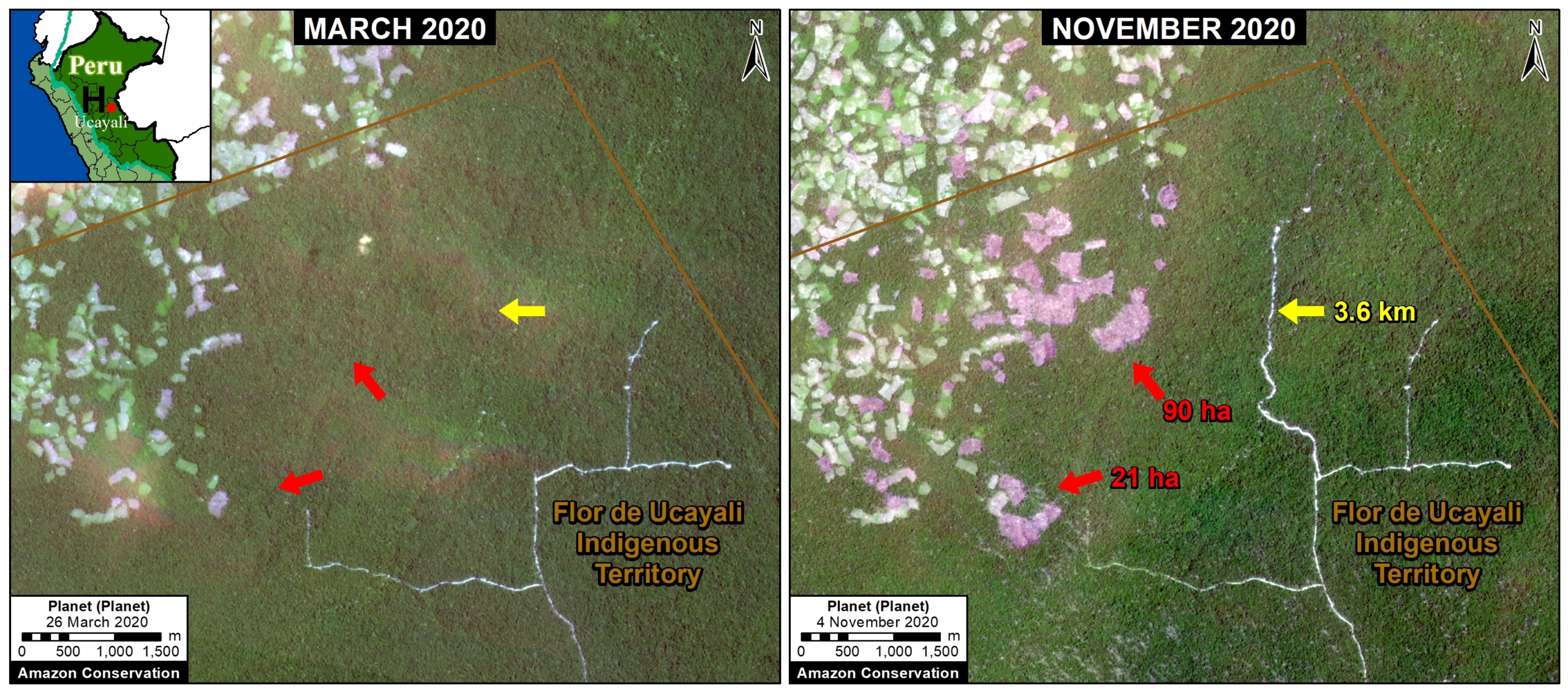
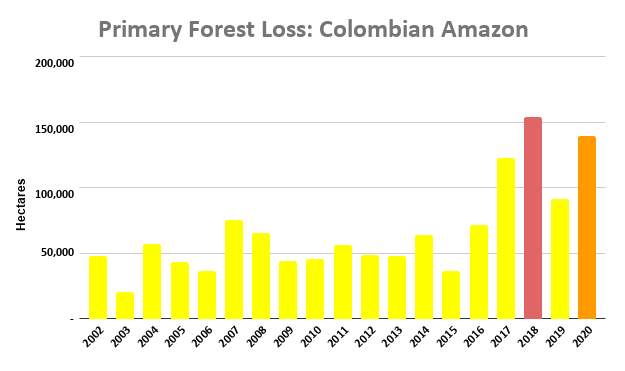
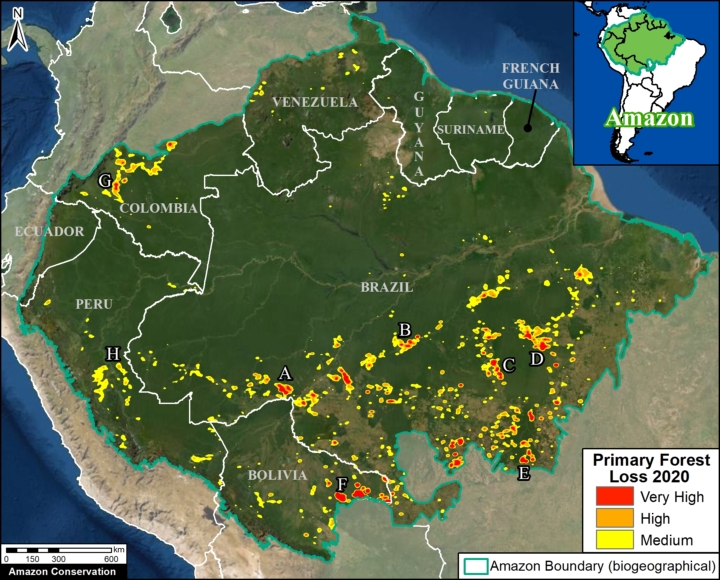
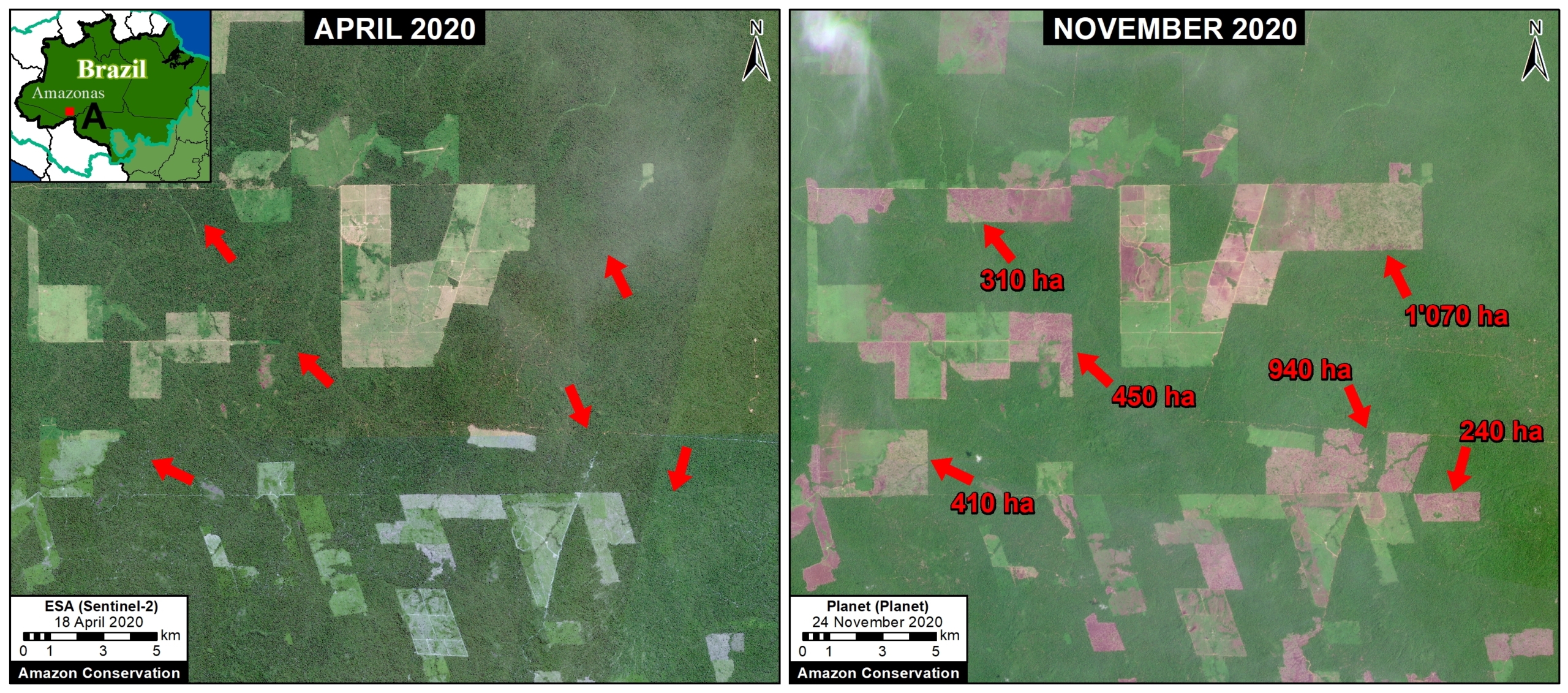
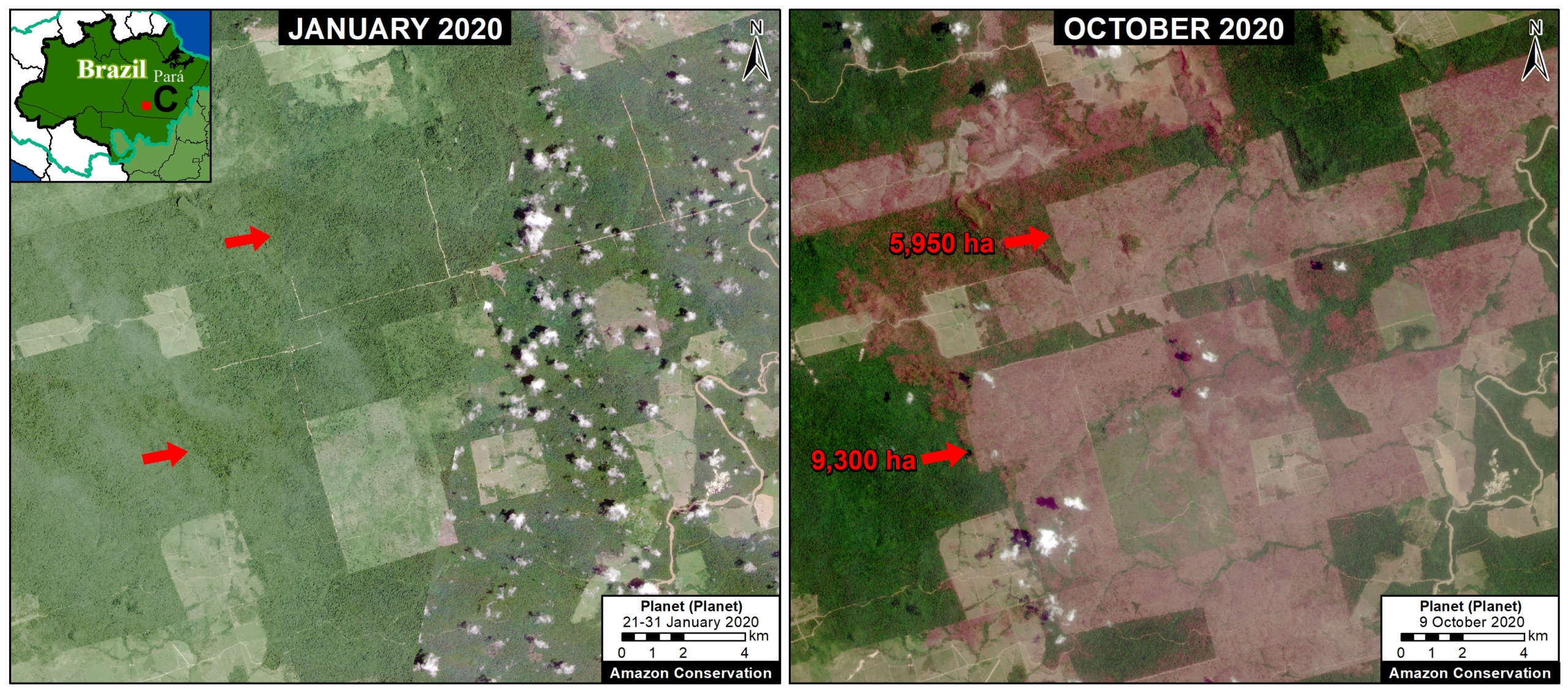
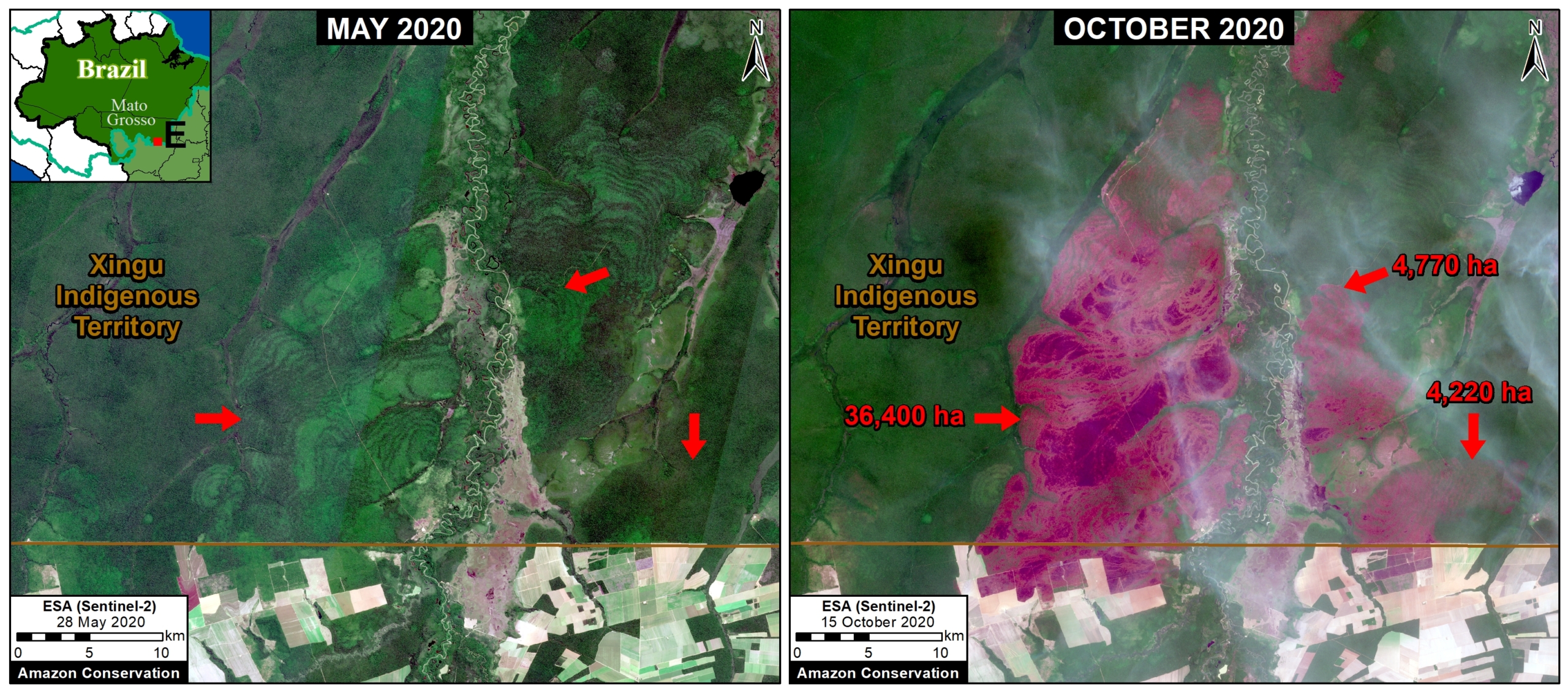
Extensive deforestation, especially along the major road networks, has shockingly turned the eastern Brazilian Amazon into a net carbon source (see MAAP #144).
Fortunately, the greater Amazon across all nine countries is still a net carbon sink, largely thanks to the still intact core of the western Amazon.
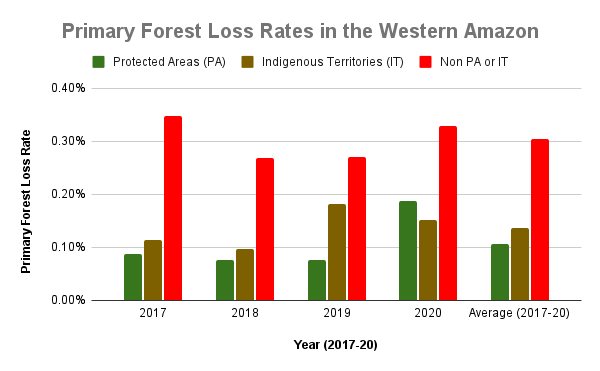
The biggest long-term threat to this core Amazon is likely new roads, as they are a leading cause of opening up vast and previously remote areas to deforestation and degradation (Vilela et al 2020).
Here, we present an initial analysis of new and proposed roads across the western Amazon.
Although it’s difficult to predict what proposed projects are actually likely to eventually move forward, we do find the potential of a major road expansion across the core western Amazon (see Base Map 1).
Moreover, even by just focusing on the most advanced or actively discussed projects, we find the risk of major negative impact.
Below, we discuss our initial Amazon Roads Base Map and present a series of zooms showing the primary forest at risk if select road projects move forward.
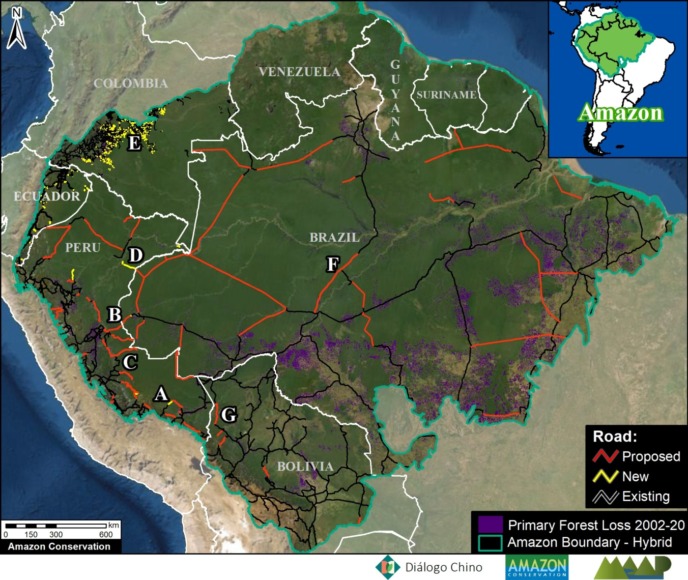
Amazon Roads Base Map
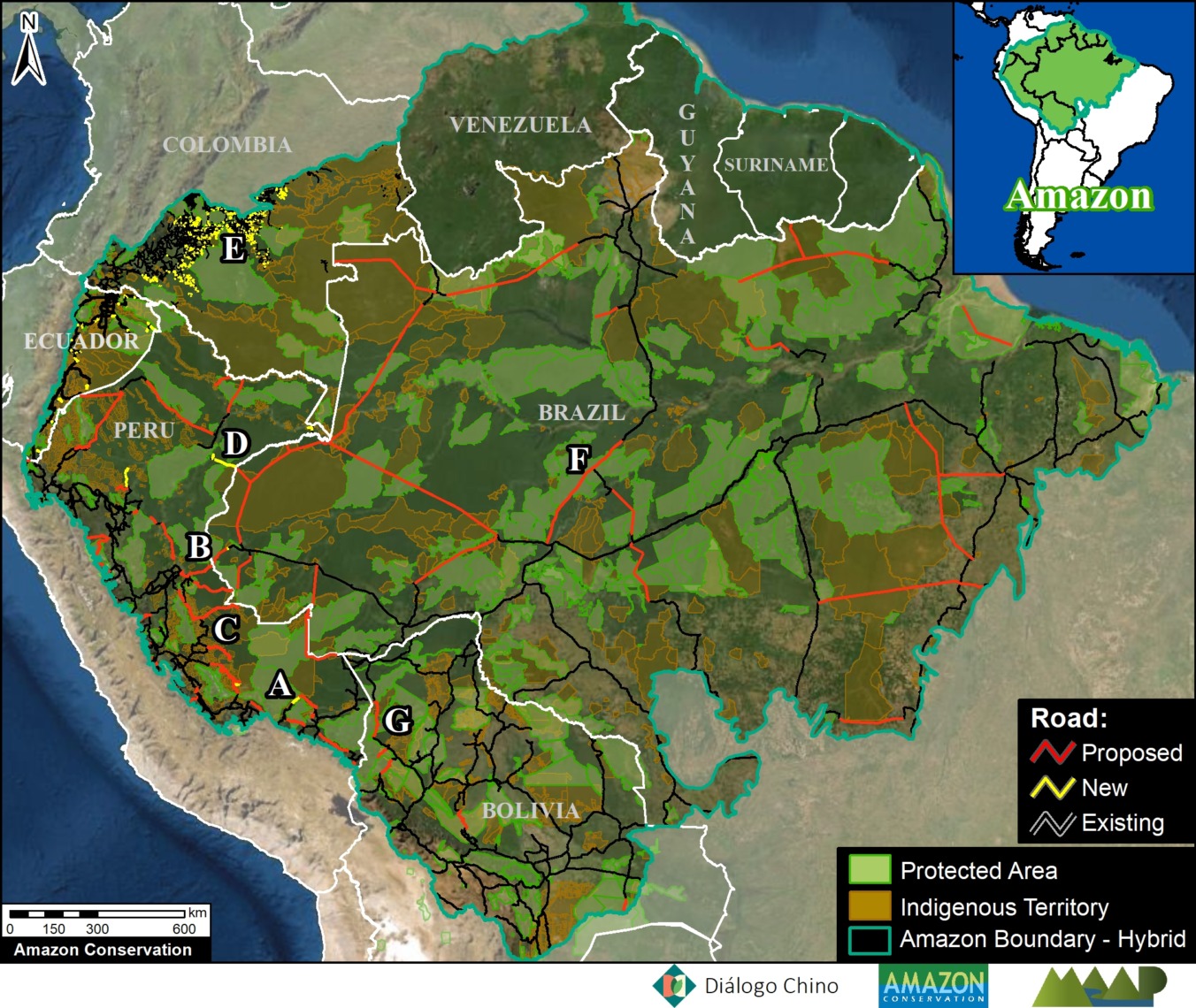
Base Map 2 highlights new, proposed, and existing roads (red, yellow, and black lines, respectively), in relation to protected areas and indigenous territories for context. We focus on the still largely intact core of the western Amazon (Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and western Brazil).
Most of the new roads were constructed in the past five years and were digitized from satellite imagery. Note that for some of these new roads, just initial construction of a rough road started and there is still potential for future impacts from road improvement and paving.
Most of the proposed roads were obtained from official government data sets. As noted above, it’s difficult to predict what proposed road projects are actually likely to eventually move forward. Nonetheless, it is clear to see there is the potential to greatly divide the remaining core western Amazon with the portfolio of proposed roads.
Zooms of High-Impact New & Proposed Roads
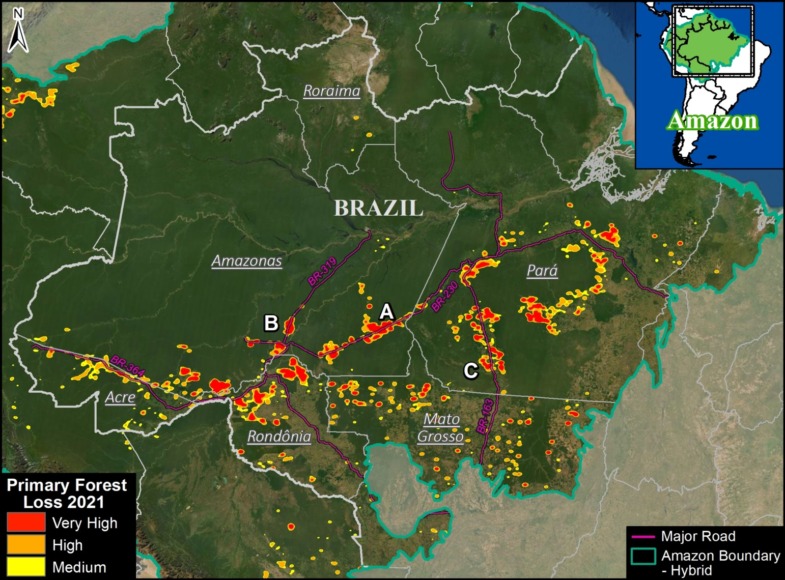
In this section, we focus on the currently most advanced or actively discussed projects (see Letters A-F on Amazon Roads Base Map). We highlight their potential impacts to vast sections of the core western Amazon protected areas and indigenous terrritories.
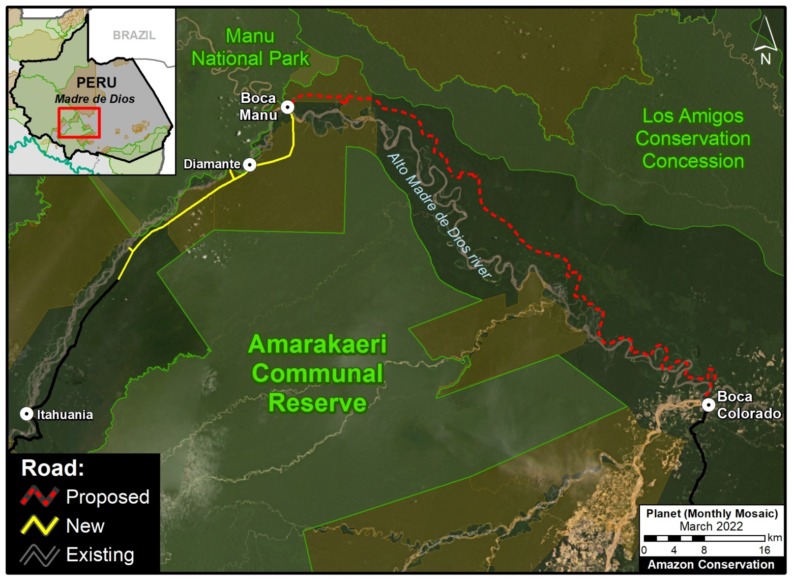
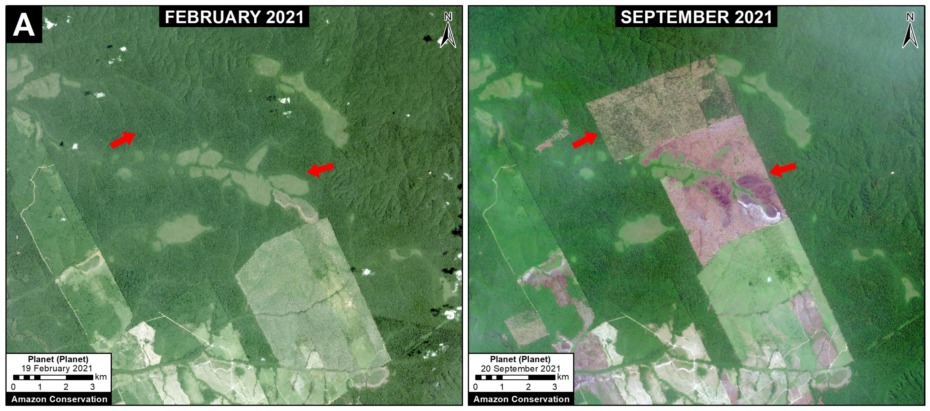
A. Boca Manu Road (Peru)
The new/proposed road that we refer to here as the Boca Manu road would serve as a new connection between Cusco and Madre de Dios regions. It is notable due its sensitive route between Manu National Park and Amarakaeri Communal Reserve to Boca Manu, and from there between Los Amigos Conservation Concession and Amarakaeri Communal Reserve to Boca Colorado. In addition to likely impacting these protected areas and the concession, the road also has the potential to impact the nearby territory of indigenous groups in voluntary isolation. See this recent report from Diálogo Chino for more information about this road and its status and impacts.
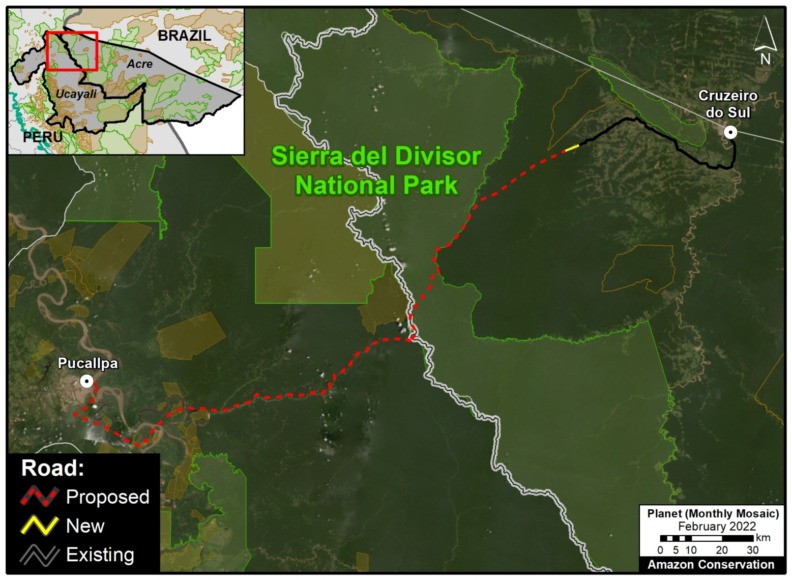
B. Pucallpa – Cruzeiro do Sul Road (Peru – Brazil)
This proposed road would connect the Peruvian city of Pucallpa with the edge of the existing road network in western Brazil, near the town of Cruzeiro do Sul. Although the potential route has several options, it would sure cut through or near Sierra del Divisor National Park in Peru and the adjacent Serra do Divisor National Park in Brazil. This area is characterized by vast primary forests, thus creating a new binational route connecting the deforestation fronts in each country could obviously trigger significant impacts. See this recent report from Diálogo Chino for more information about this road and its status and impacts.
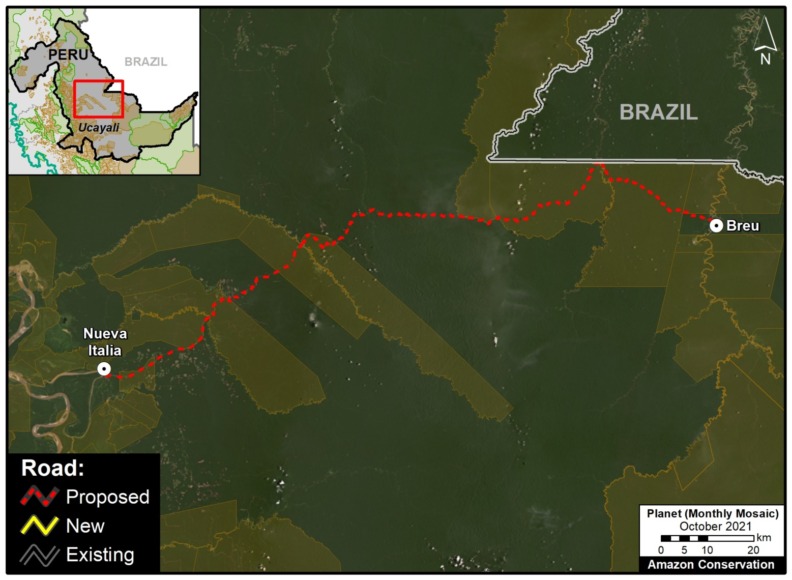
C. Yurua Road (Peru)
The new/proposed road that we refer to here as the Yurua road would connect the Peruvian towns of Nueva Italia on the Ucayali River and Breu on the Yurua River. This 200 km route was originally built as a logging road in the late 1980s to access remote timber areas in the central Peruvian Amazon, but had fallen into disrepair by the early 2000s. A recent MAAP analysis (see MAAP #146) found that between 2010 and 2021 much of the route had been rehabilitated, triggering elevated deforestation along the way. If this road were ever to be paved then impacts would likely continue to rise, including with native communities along the route. See MAAP #146 for more information about this road and its status and impacts.
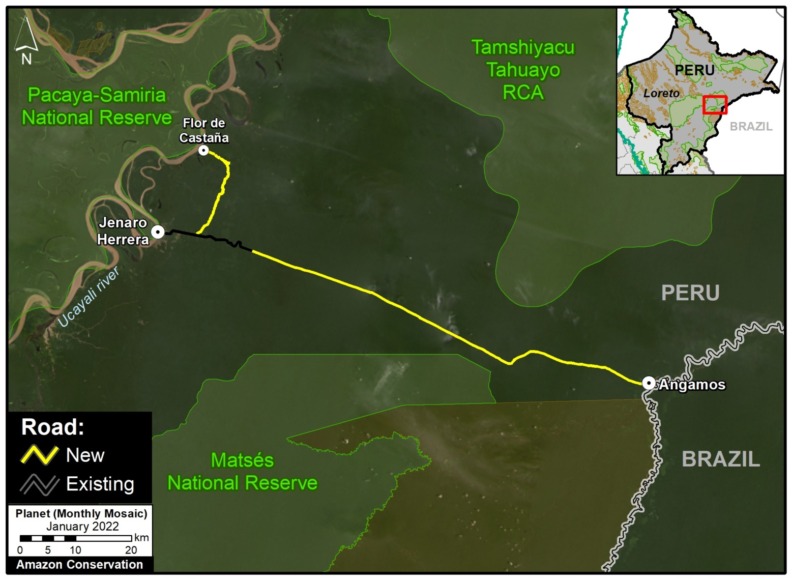
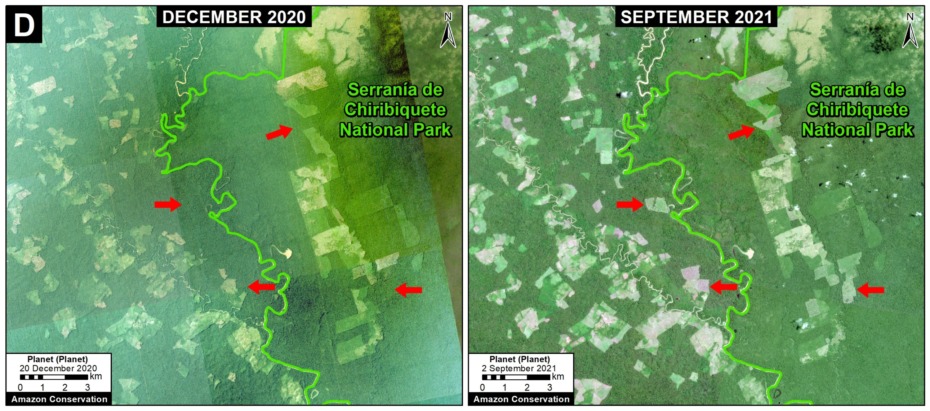
D. Genaro Herrera – Angamos Road (Peru)
This new/proposed road would build off an old track through the vast forests connecting the northern Peruvian towns of Genaro Herrera and Angamos, in the region of Loreto. In 2021, clearing began along this route, advancing over 100 kilometers from both ends. If completed and paved, the final road project would impact protected areas on both sides (including the Matsés National Reserve to the south) and pose a major threat to indigenous people in voluntary isolation reportedly living to the north. See this recent report for more information about this road and its status and impacts.
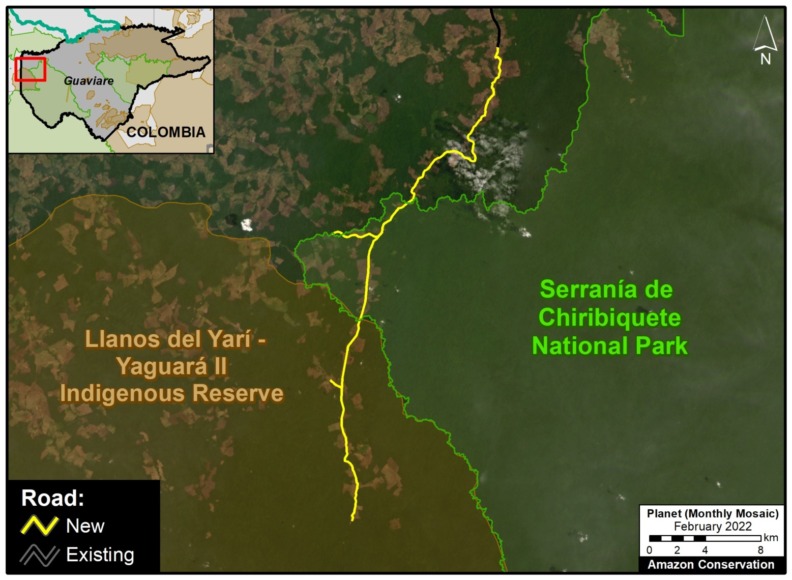
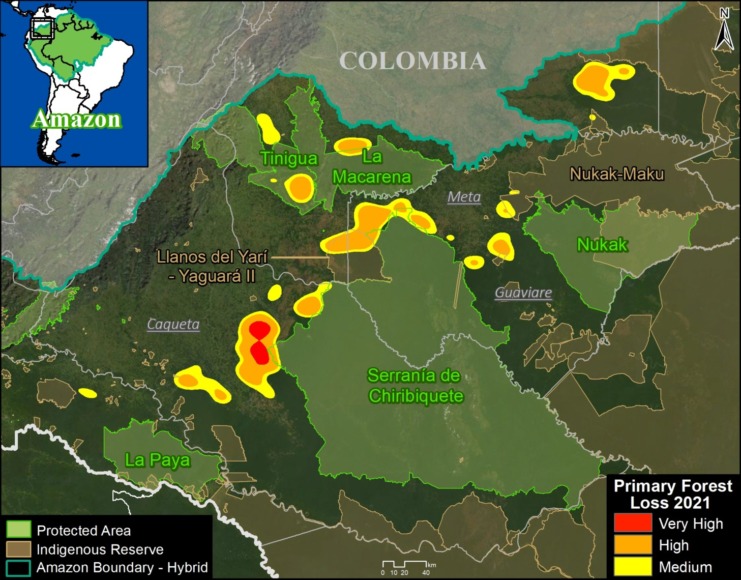
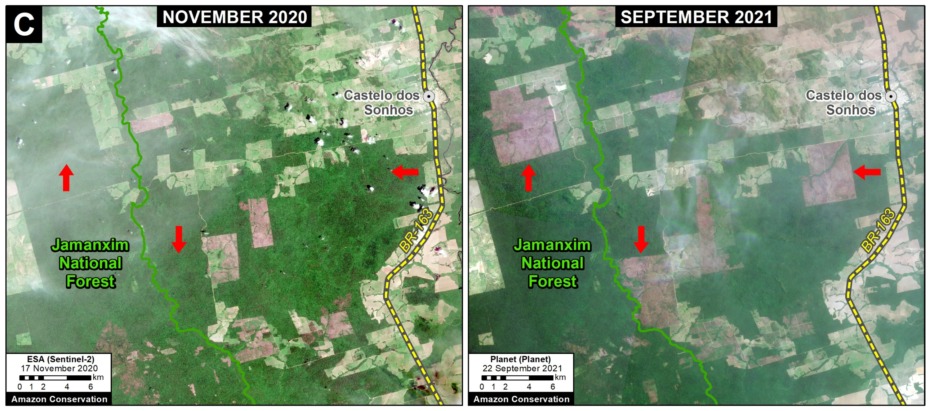
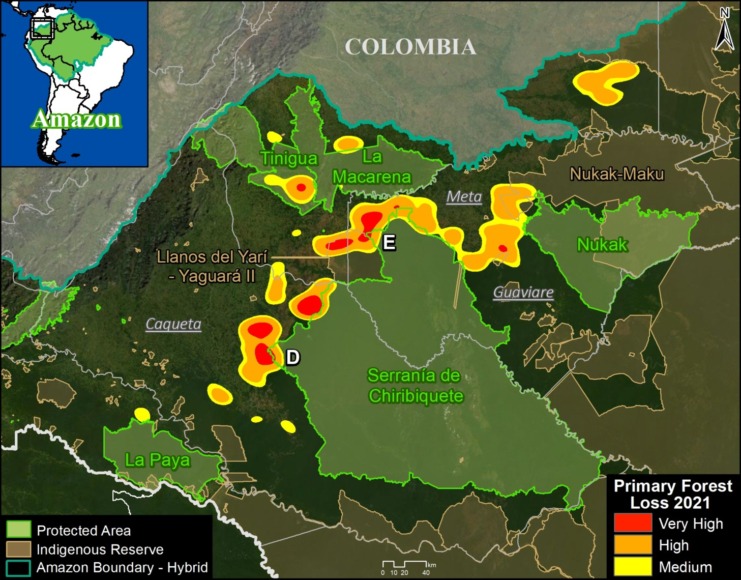
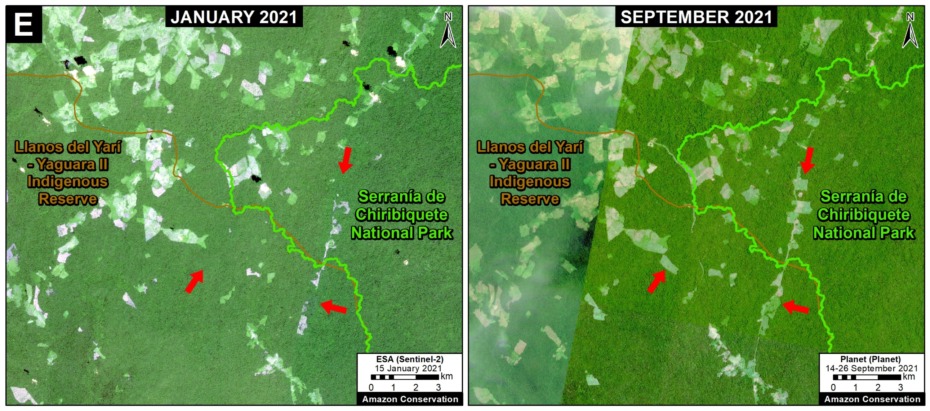
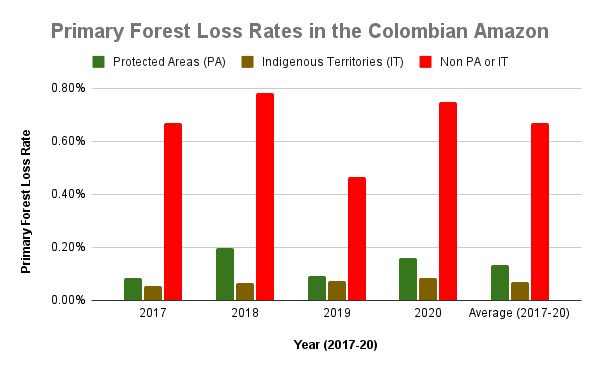
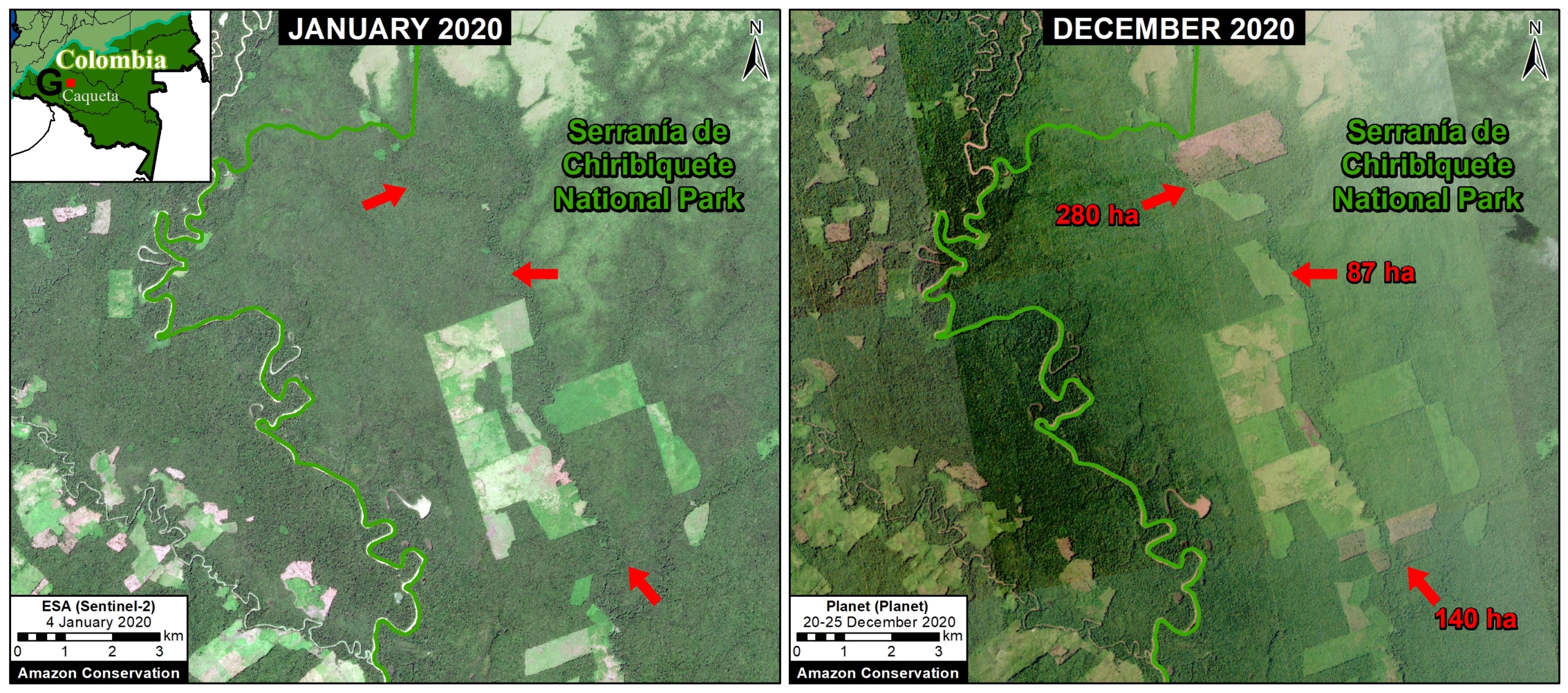
E. Cachicamo – Tunia Road (Chiribiquete National Park, Colombia)
Chiribiquete National Park, located in the heart of the Colombian Amazon, has been experiencing increasing deforestation pressures, partly due to expanding road networks around and even within the park. For example, the Cachicamo-Tunia Road, constructed in 2020, has triggered a new deforestation front in the northwest section of the park. Note this road is also impacting an adjacent Indigenous Reserve.
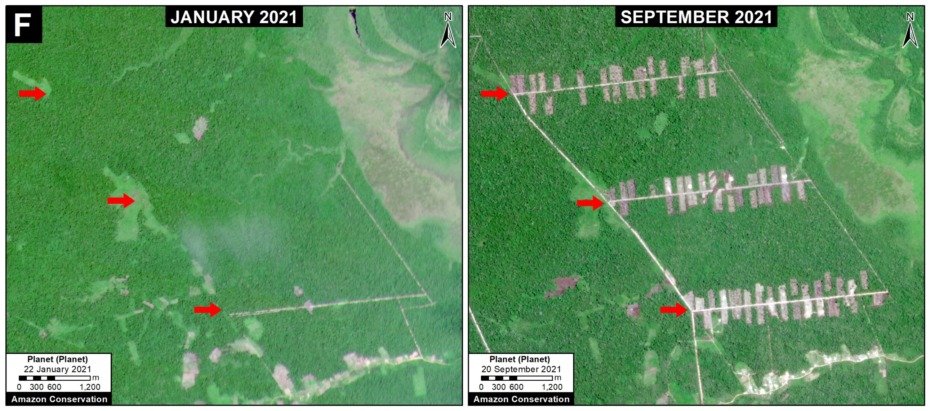
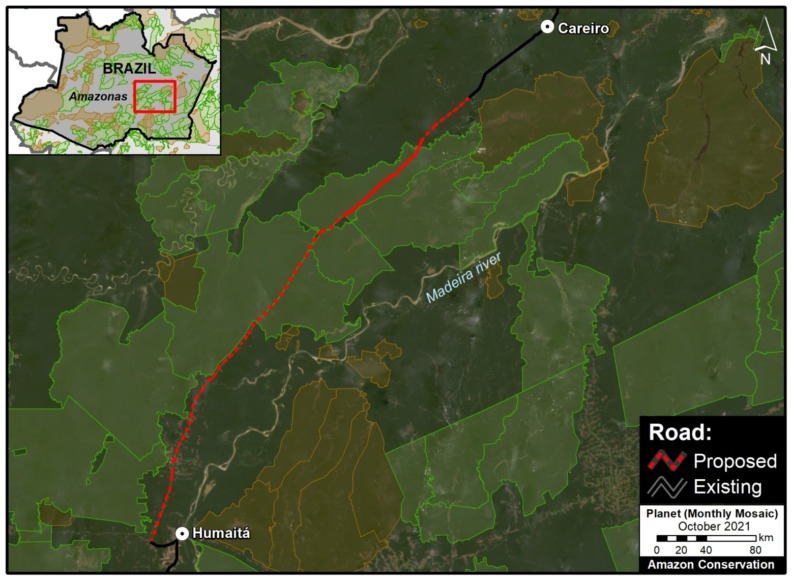
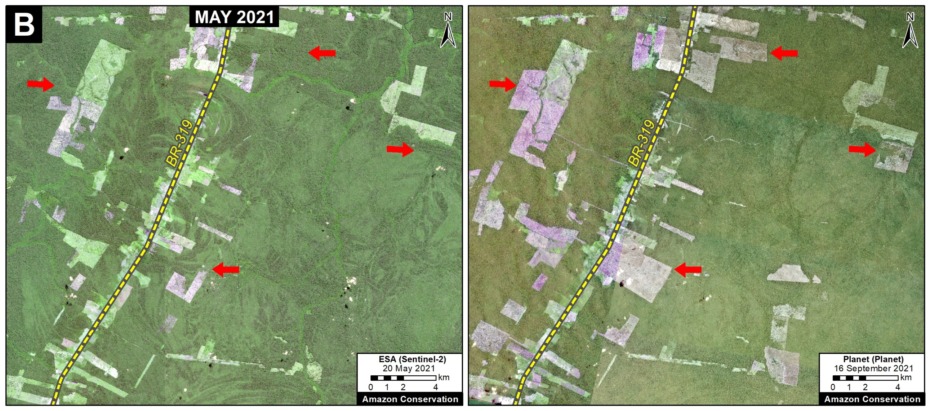
F. Manaus – Porto Velho Road (BR-319, Brazil)
Arguably the most controversial project on the list: paving the middle section of BR-319 in the heart of the Brazilian Amazon. This nearly 900 km road connects the remote city of Manaus (otherwise only reachable by air or water) with the rest of Brazilian road network in Humaitá and Porto Velho to the south. It was built in the early 1970s but abandoned and impassable by the late 1980s, isolating Manaus once again. Since 2015, a basic maintenance program has made the road generally passable, but the main project remains: paving the 400 km middle section that passes through the core western Amazon. This paving would effectively connect Manaus with the existing highways in the south, and most likely trigger massive forest loss by extending the arc of deforestation northwards, including within and around the protected areas that surround the road. This road project has been the subject of numerous recent press reports, including investigative pieces by the Washington Post and El Pais.
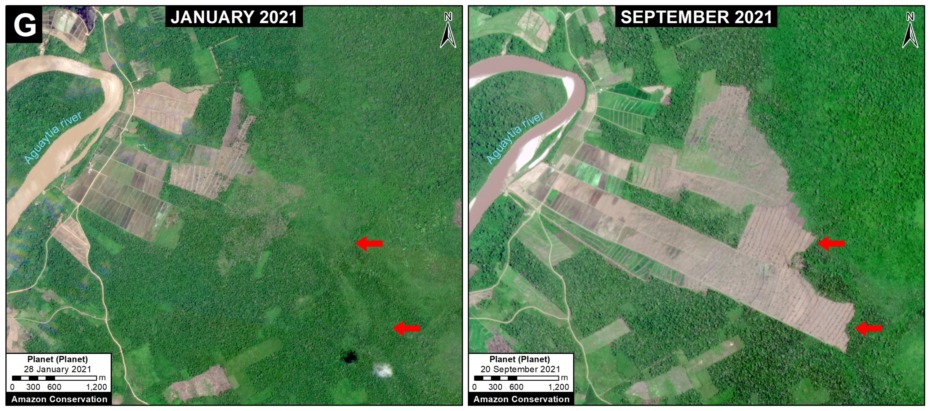
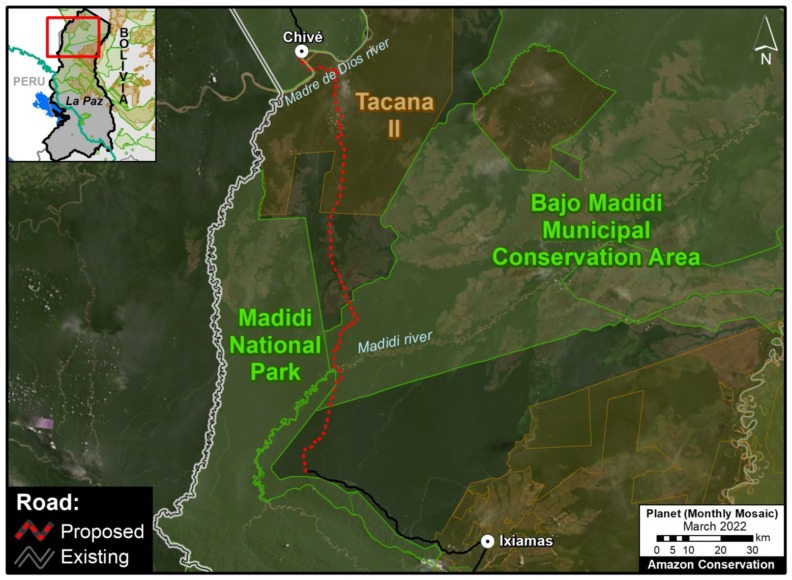
G. Ixiamas – Chivé Road (Bolivia)
In recent years, Bolivia has been seeking financing for a 250 km road linking the current frontier town Ixiamas with the isolated town Chivé, located near the Peruvian border on the Madre de Dios river. This road would cross extensive tracts of primary Amazon forest and savannah in the north of the La Paz department, including the newly created Bajo Madidi Municipal Conservation Area and the Tacana II indigenous territory.
Methodology
Our analysis and maps focus on the western Amazon (Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and western Brazil).
Most of the new roads were constructed in the past five years and were digitized from satellite imagery. Note that for some of these new roads, just initial rehabilitation/improvement of a rough road started and there is still potential for future impacts from paving.
Most of the proposed roads were obtained from official government data sets (and complemented by civil society reports).
We credit the following data sources: Ministerio de Transportes y Comunicaciones (Peru), Geobosques/MINAM (Peru), Ministério da Infraestrutura (Brazil), Autoridad de Fiscalización y Control Social de Bosques y Tierra – ABT (Bolivia), Gobierno Autonomo Descentralizado Provincial de Napo (Ecuador), Fundación para la Conservación y el Desarrollo Sostenible – FCDS (Colombia), Fundación EcoCiencia (Ecuador), Diálogo Chino, Conservation Strategy Fund, RAISG, Conservación Amazónica – ACCA (Peru), Conservación Amazónica – ACEAA (Bolivia), and Amazon Conservation (digitalization of some new and proposed roads).
Reference:
Vilela et al (2020) A better Amazon road network for people and the environment. PNAS 17 (13) 7095-7102.
Acknowledgments
We especially thank Diálogo Chino for their support of this report. We also thank E. Ortiz, S. Novoa, S. Villacis, D. Larrea, M. Terán, and D. Larrea for helpful comments on earlier drafts of the text and images.
Citation
Finer M, Mamani N (2022) New and Proposed Roads Across the Western Amazon. MAAP: 157.