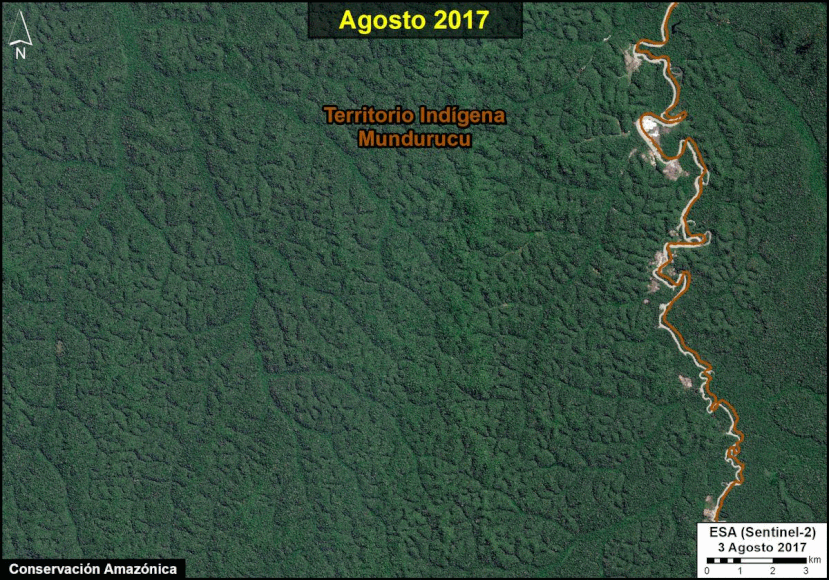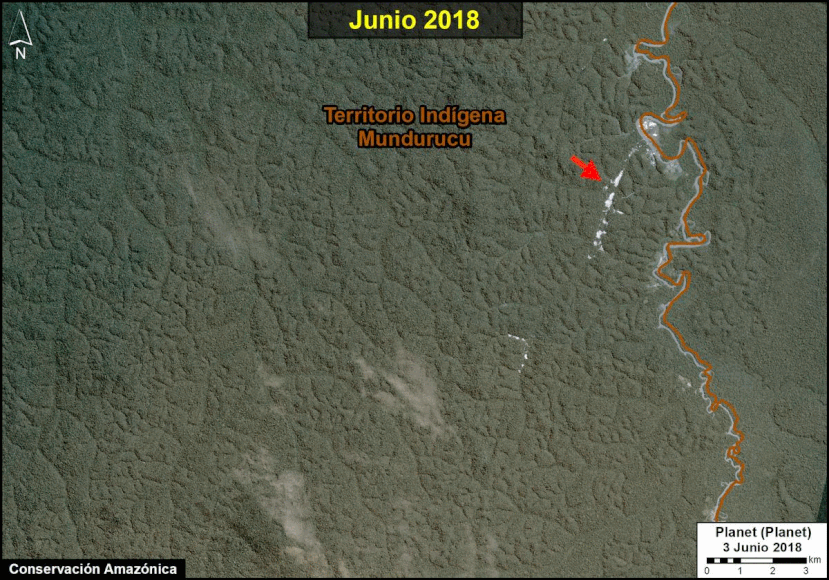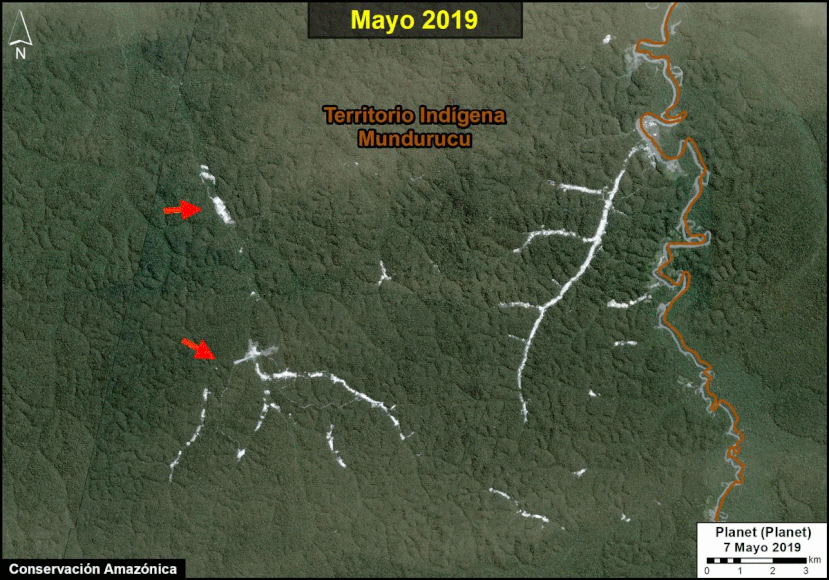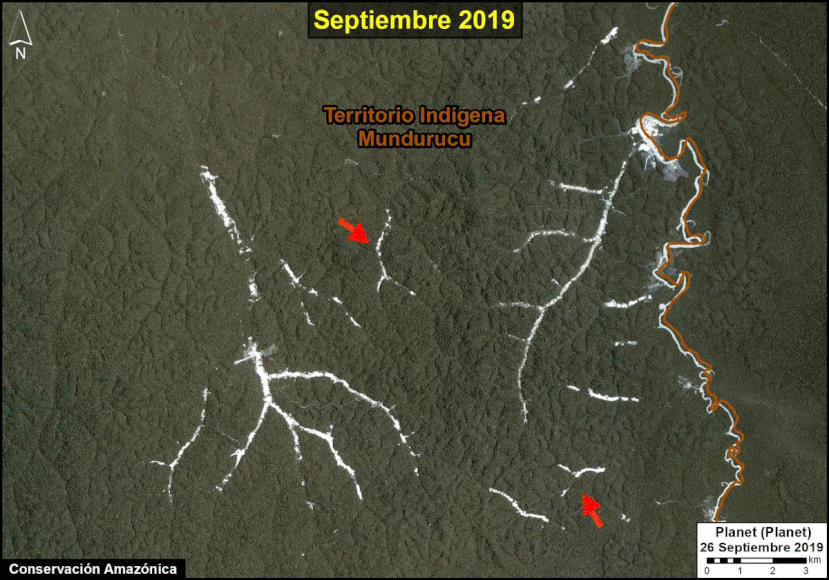
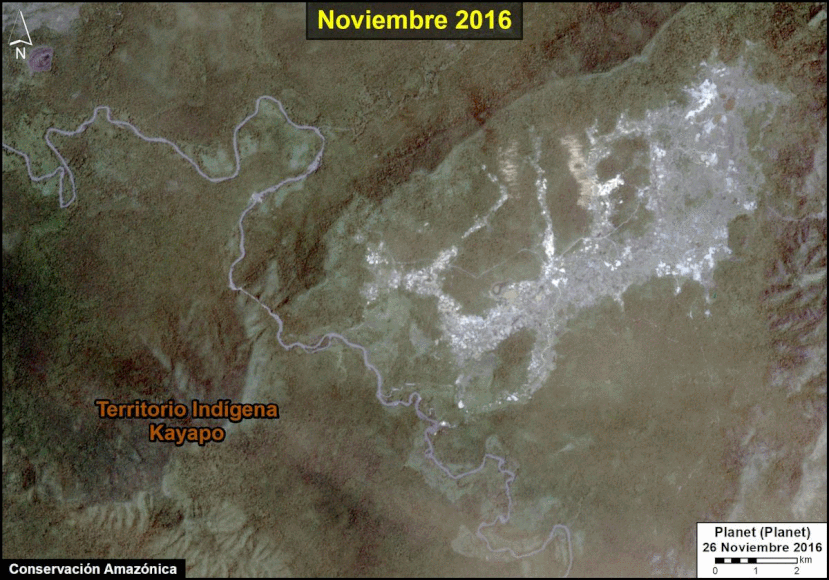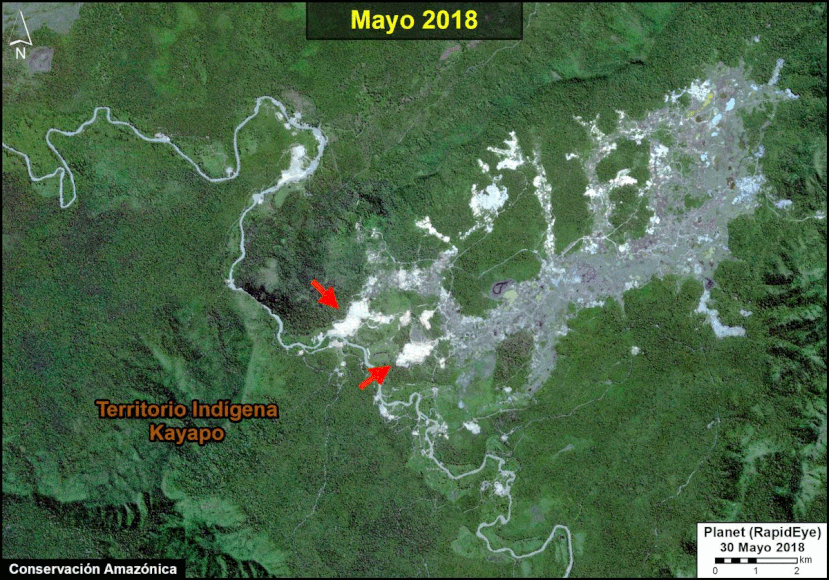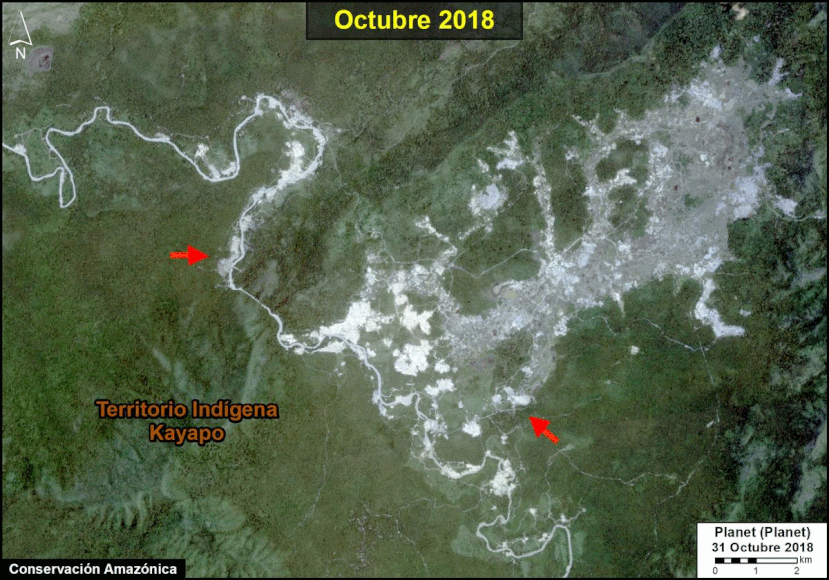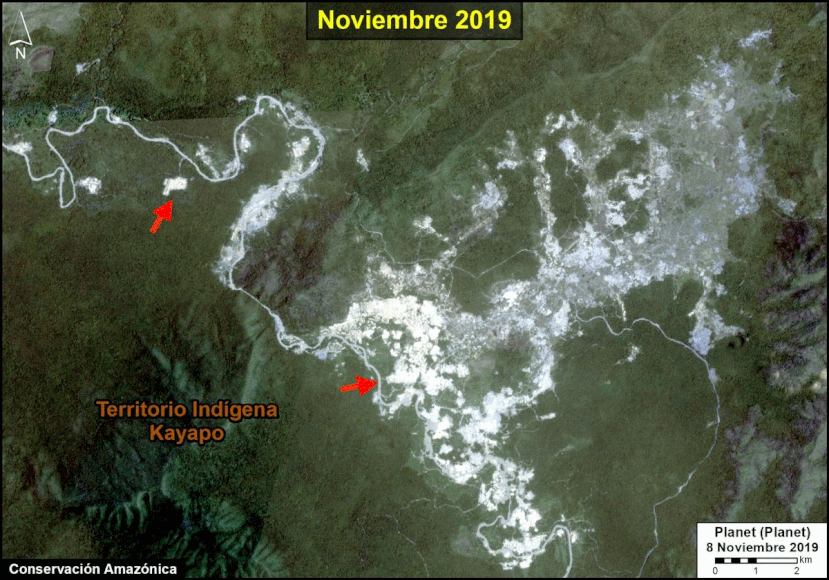
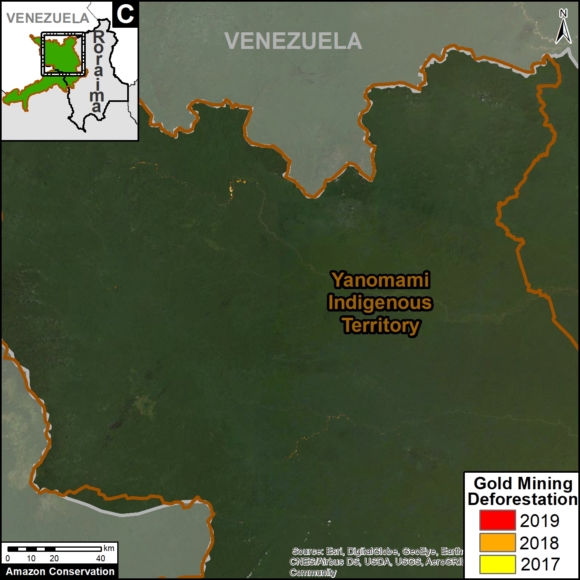
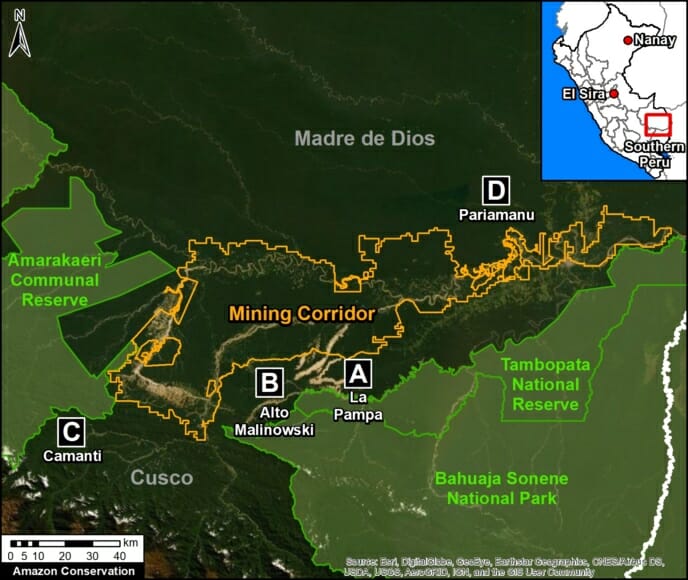
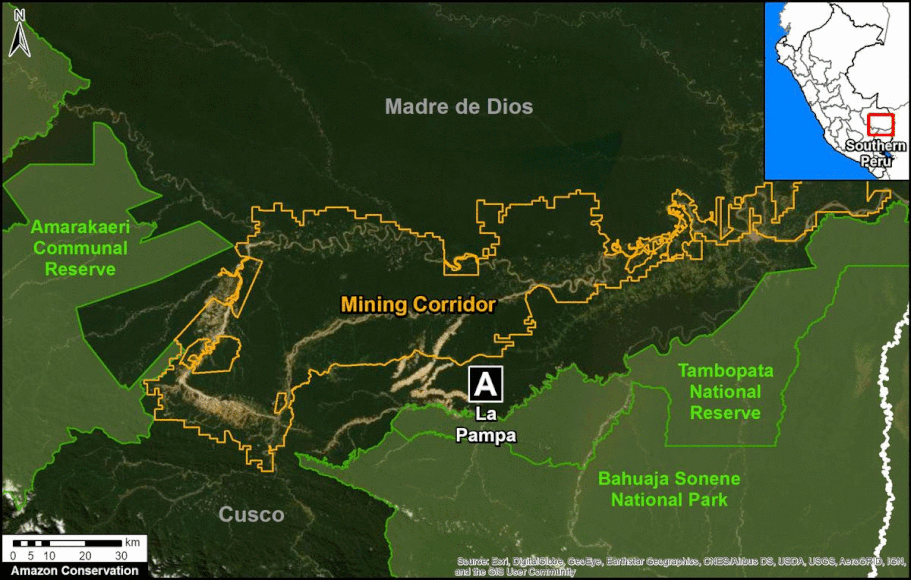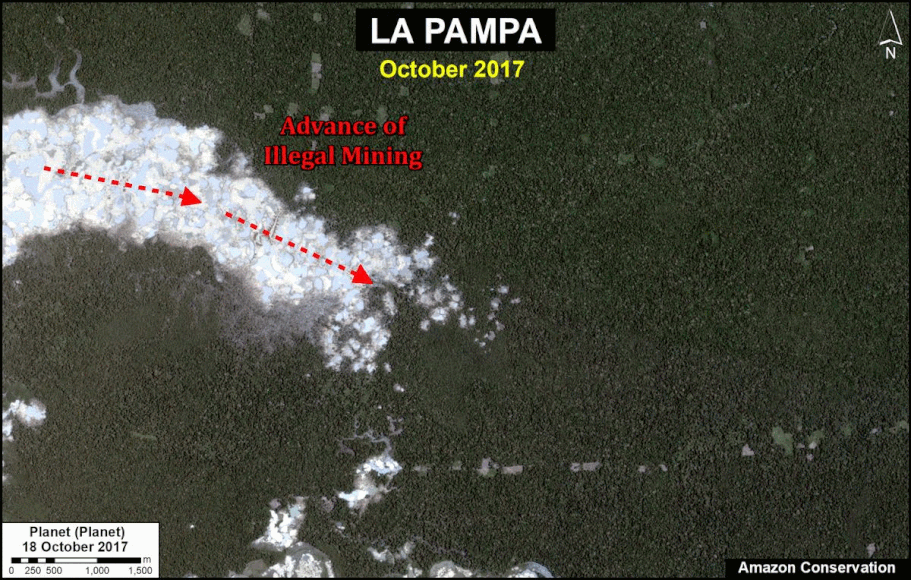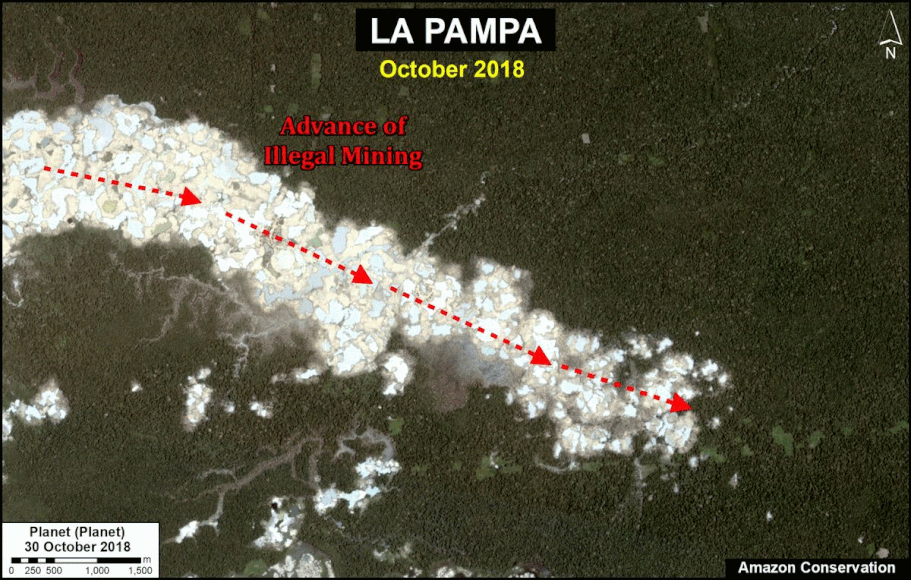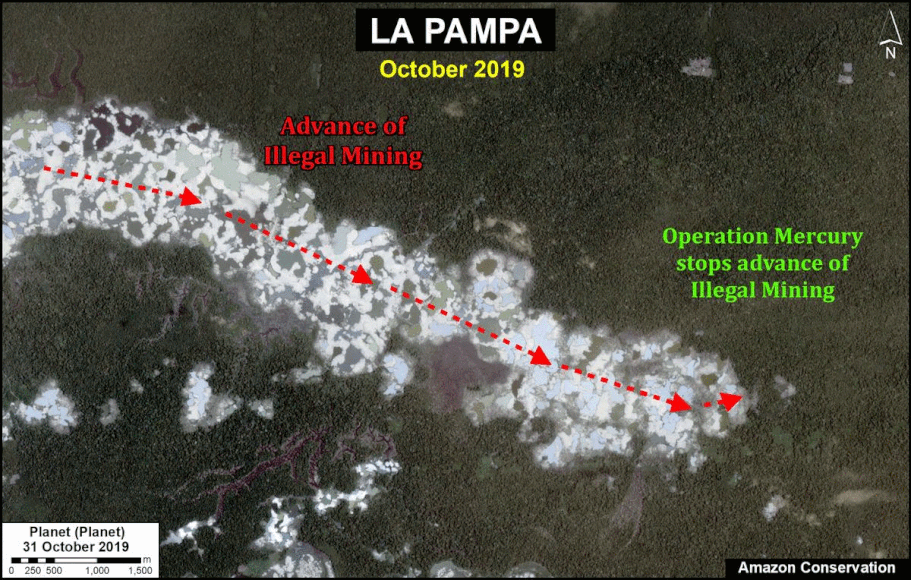
We have entered the peak deforestation season in the Peruvian Amazon, so it is also a critical time for real-time monitoring (MAAP’s specialty).
Here, we highlight the major deforestation events documented so far in 2020 (through August 23).
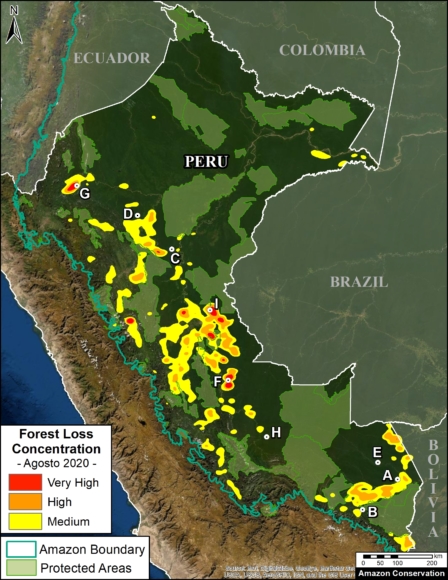
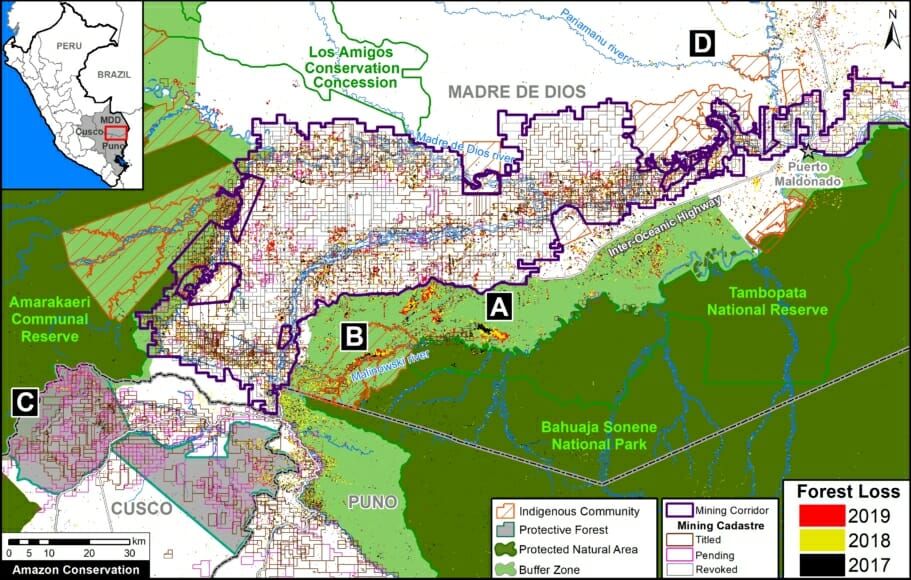
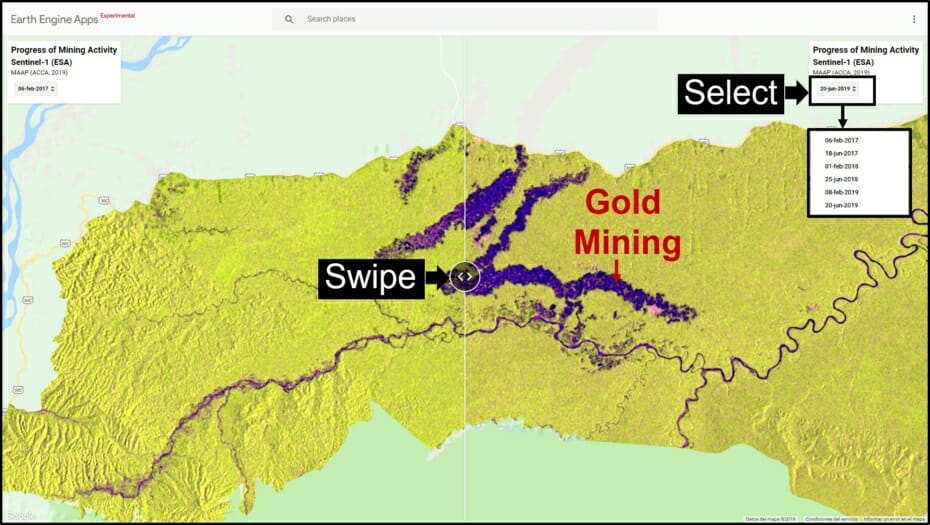
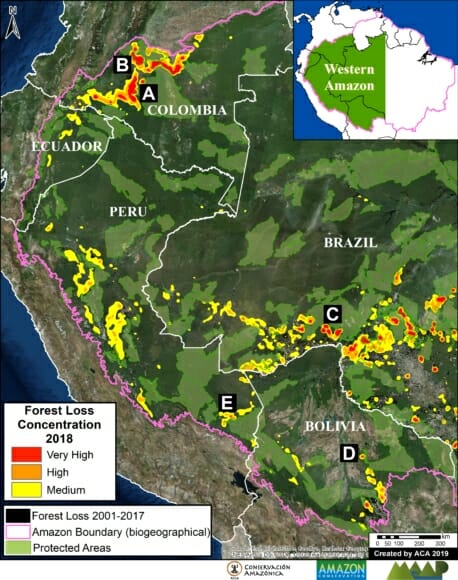
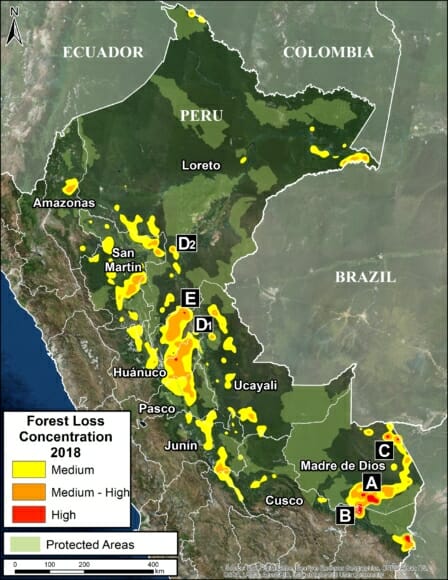
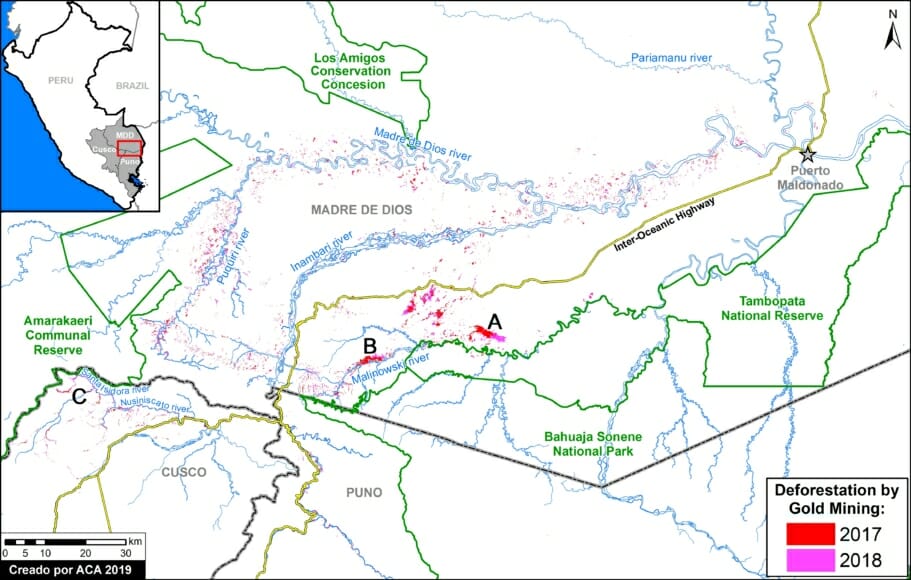
The Base Map shows the current forest loss hotspots, indicated by the colors yellow, orange and red.
Below, we present the most urgent deforestation cases, caused by gold mining and agriculture (both large and small scale), the current leading deforestation drivers in Peru.
The Letters A-I on the Base Map correspond to the location of the cases described below.
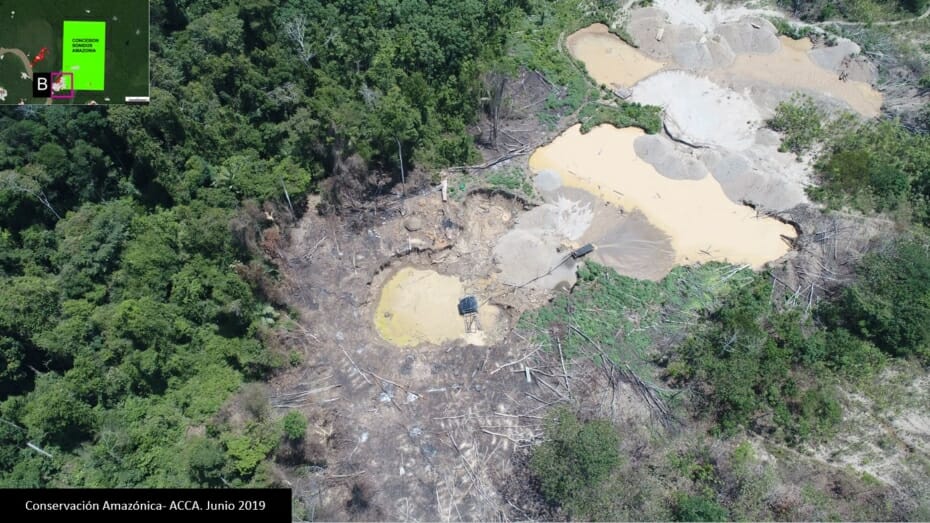
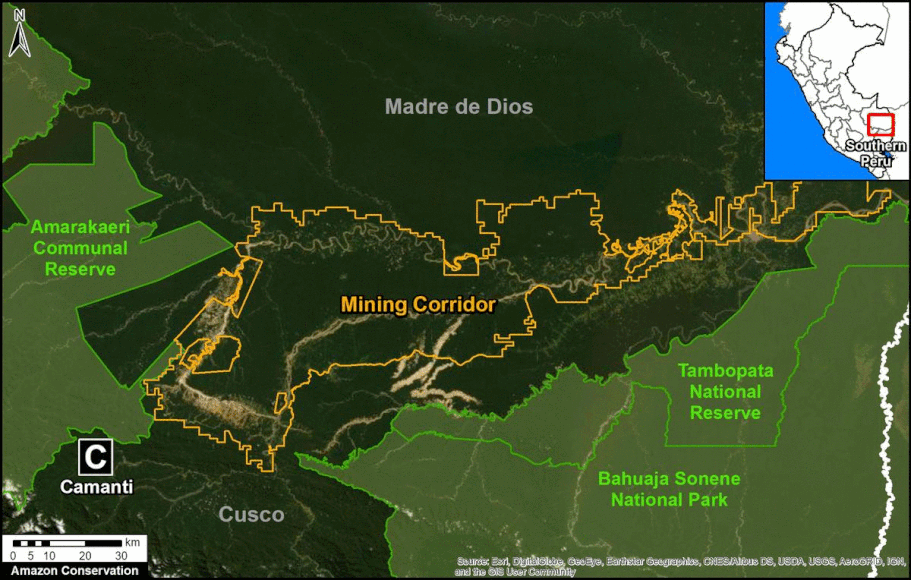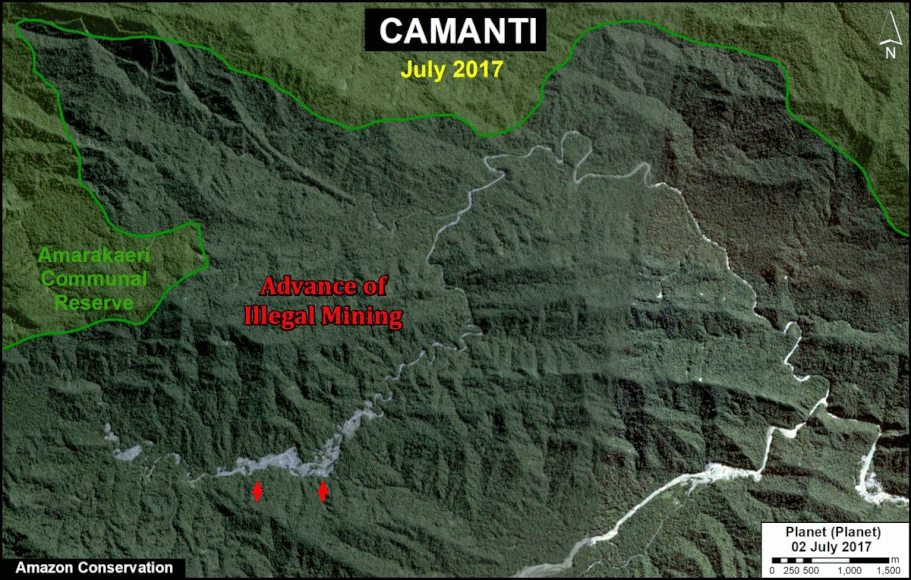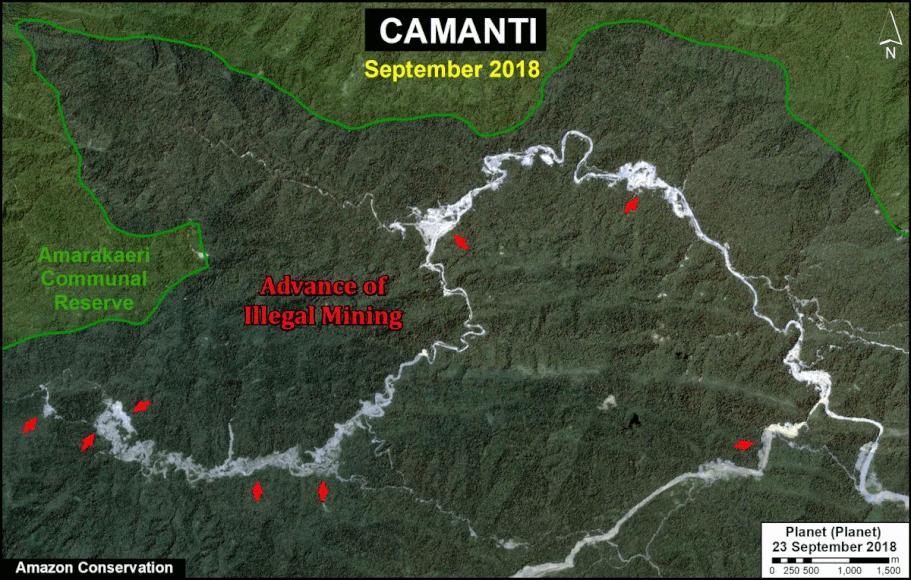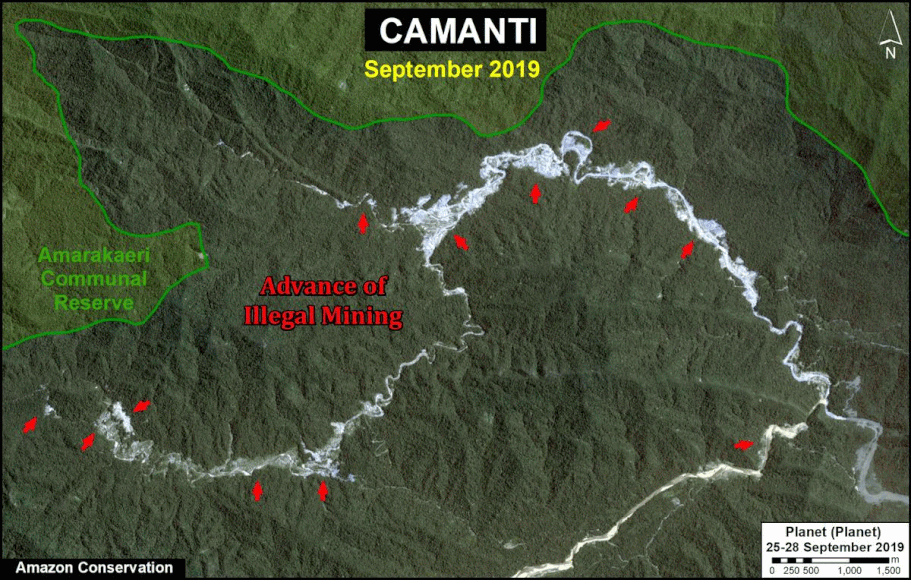
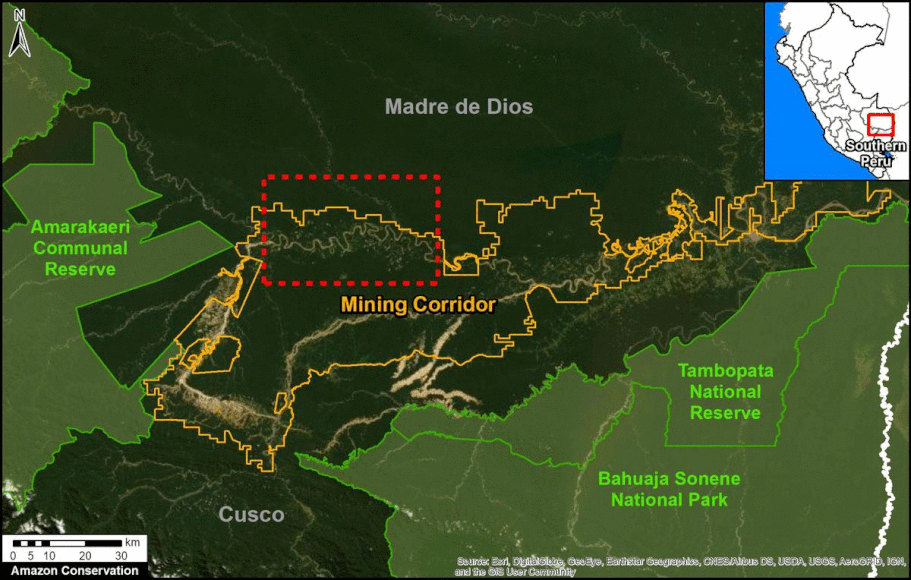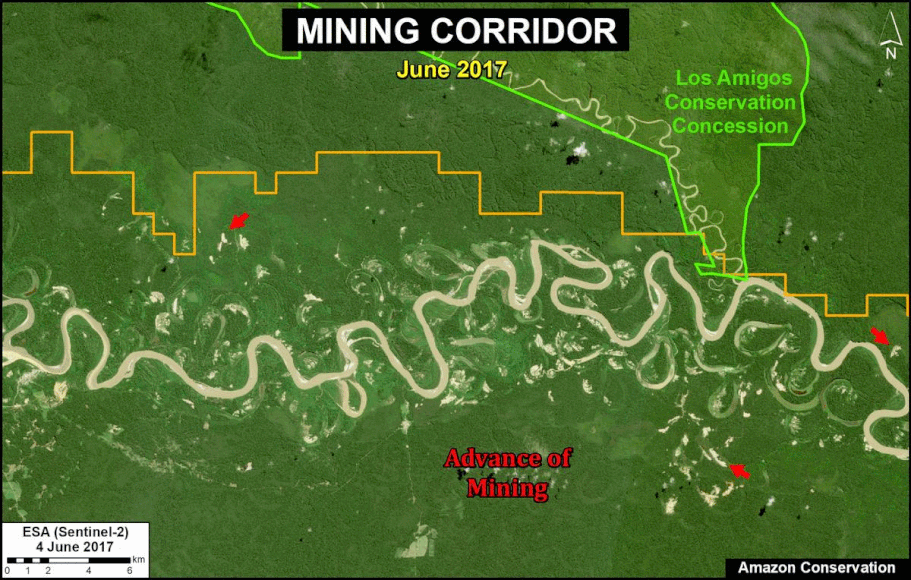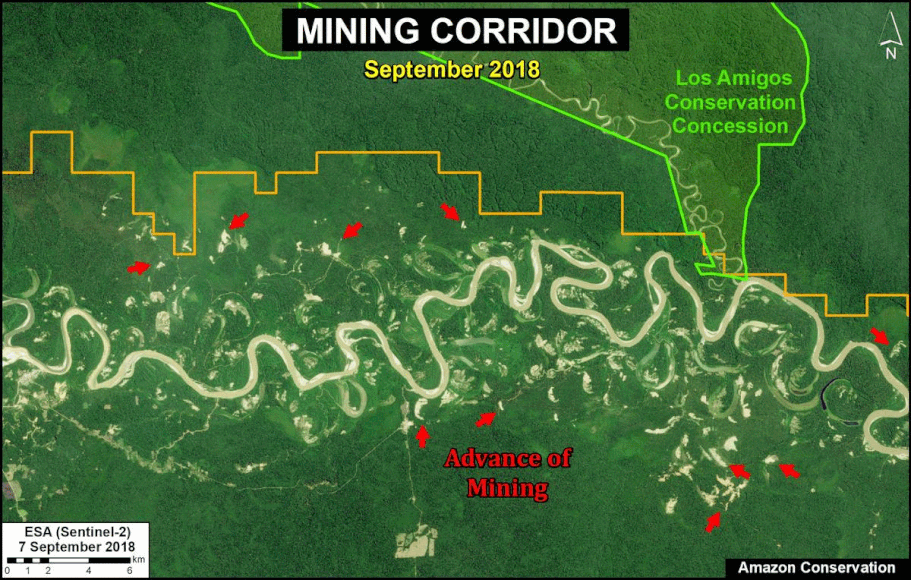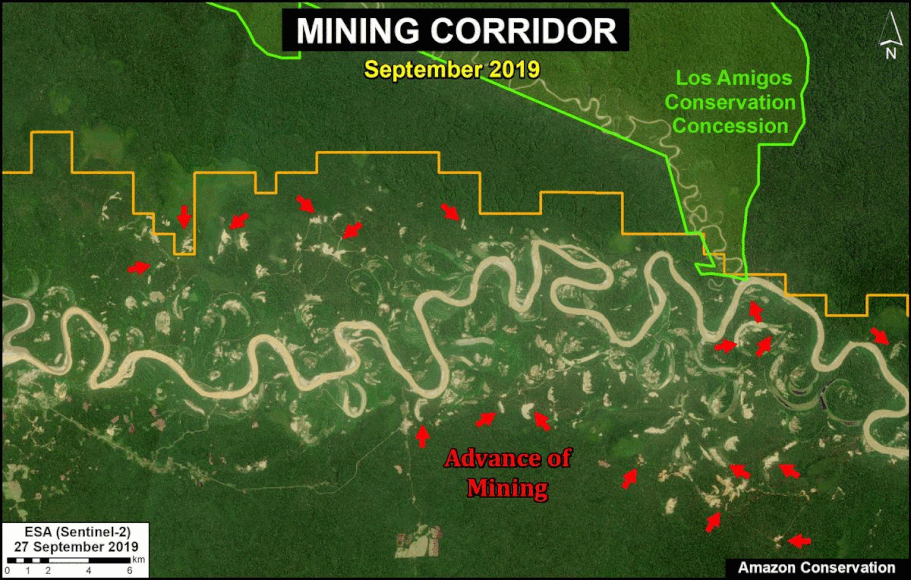
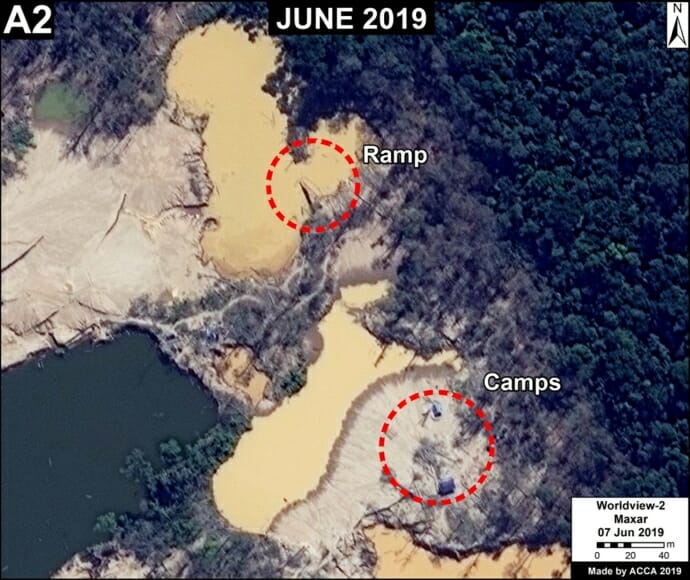
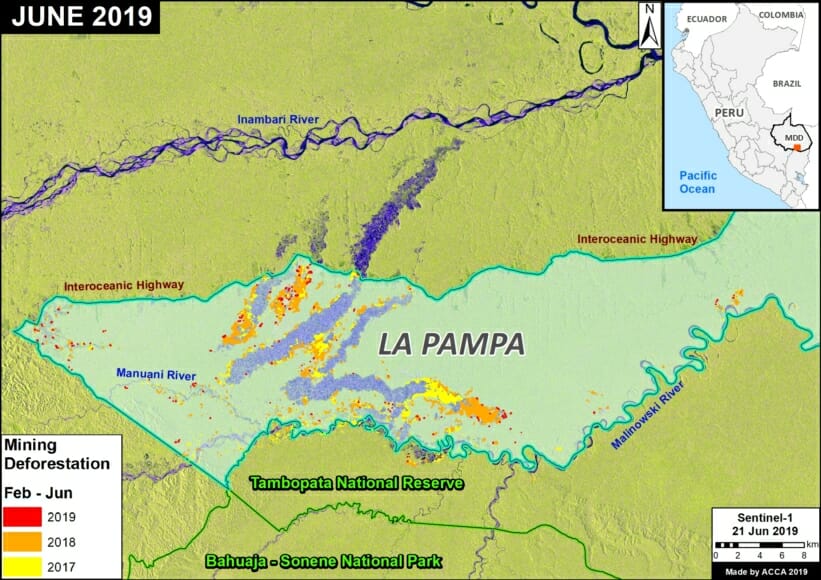
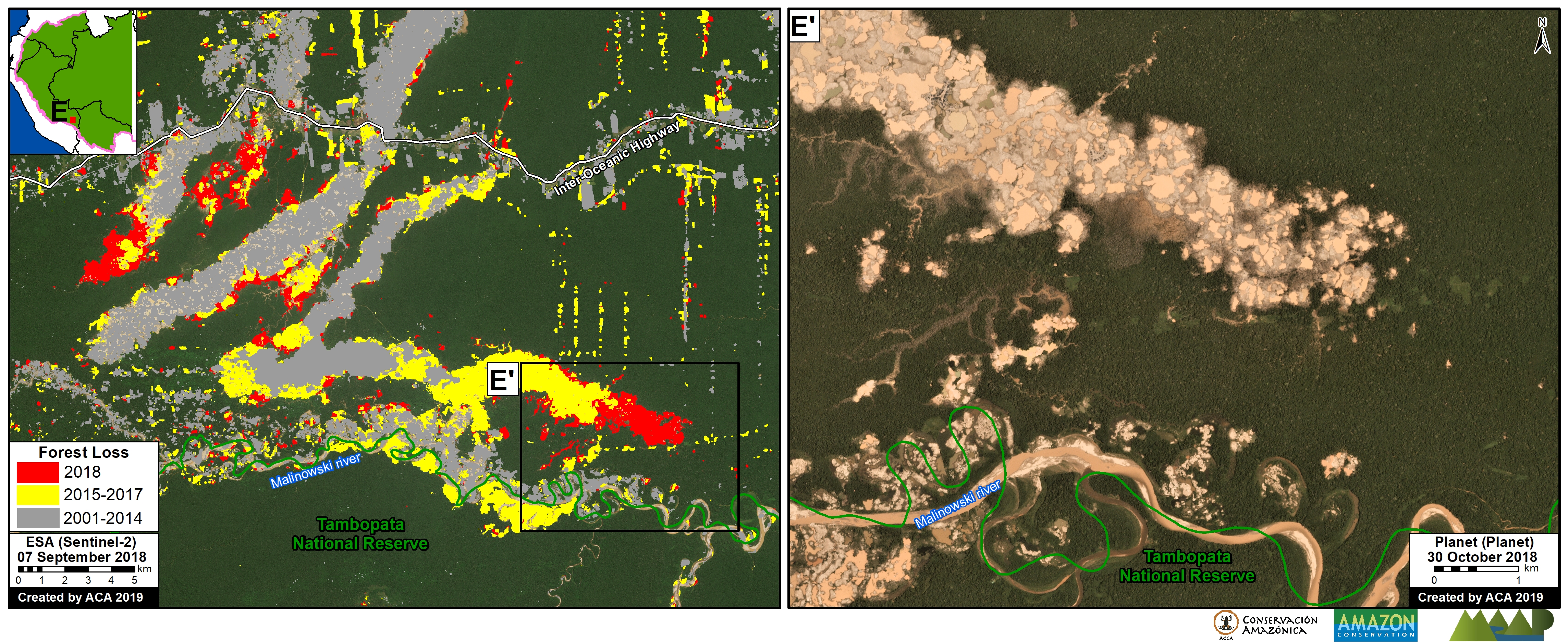
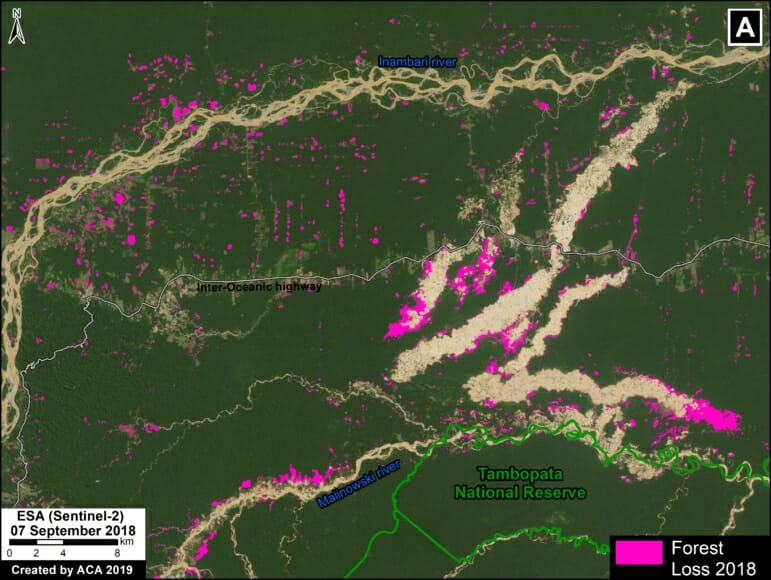
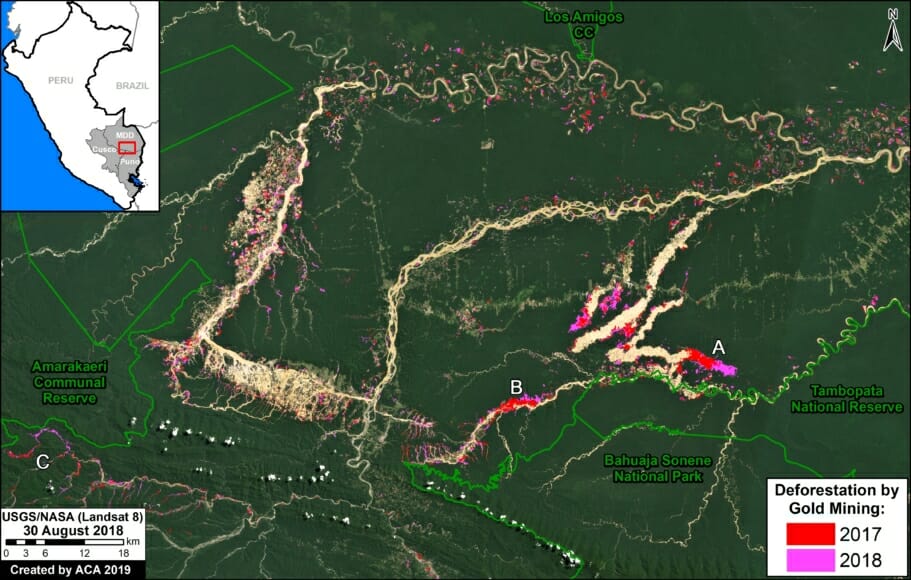
One of the key cases is the new illegal gold mining hotspot along the Pariamanu river (Letter A in the southern Peruvian Amazon).
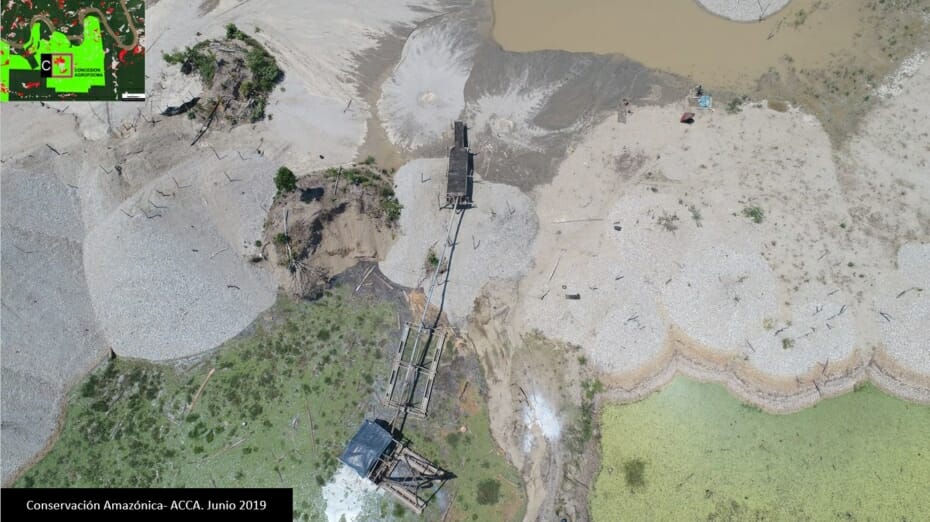
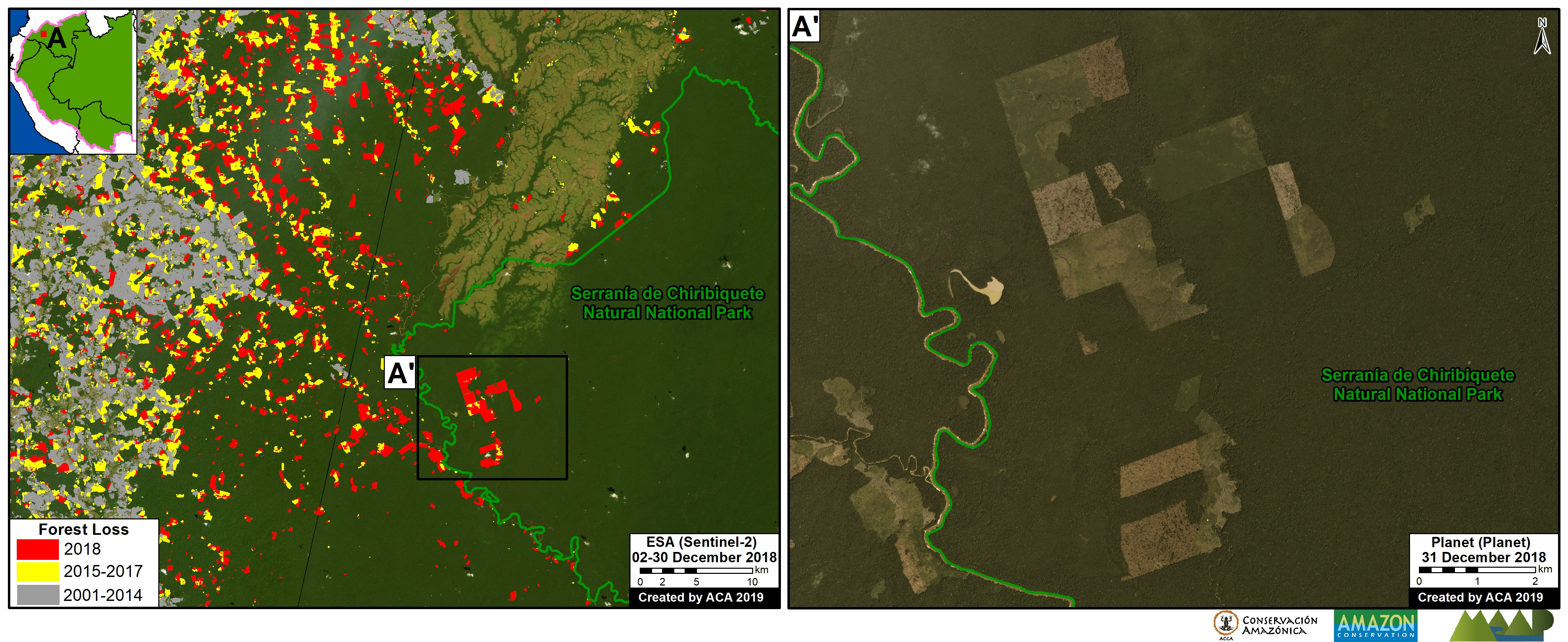
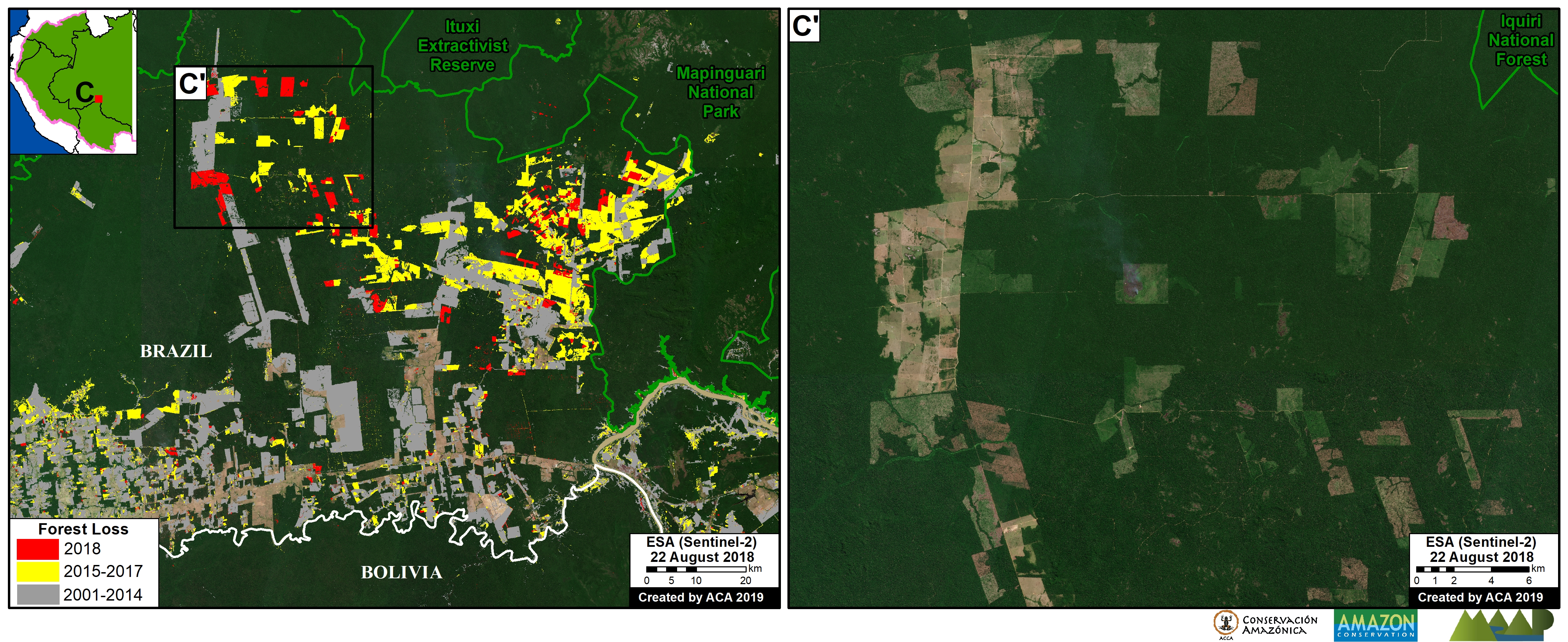
Another important case is the expanding large-scale agriculture by a Mennonite colony that continues causing an alarming deforestation.
Urgent Deforestation Cases 2020
1. Gold Mining
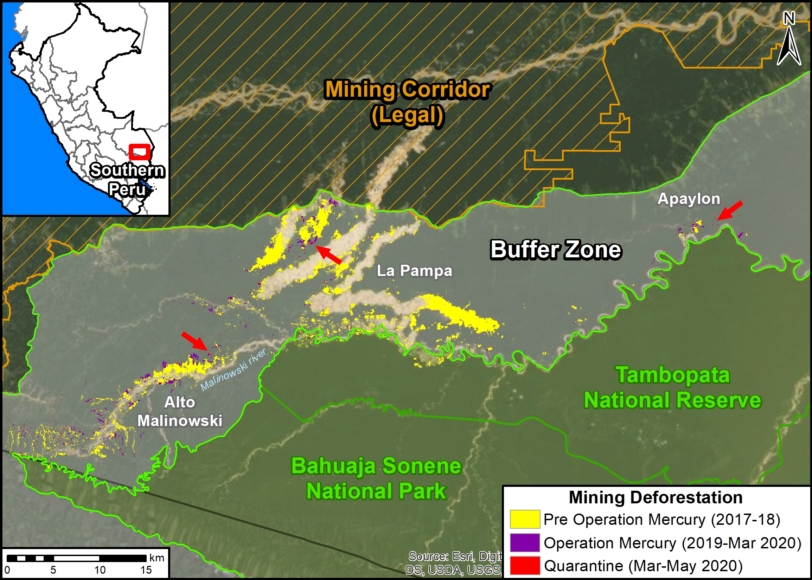
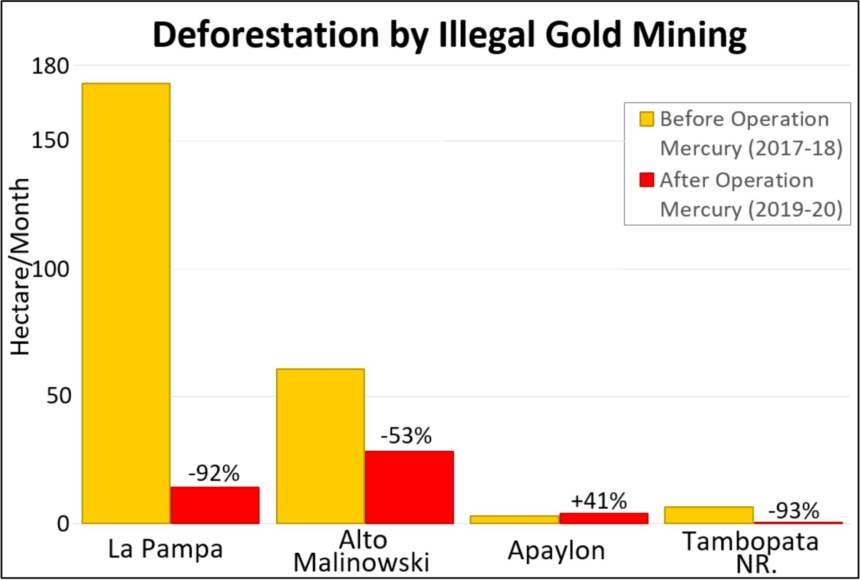
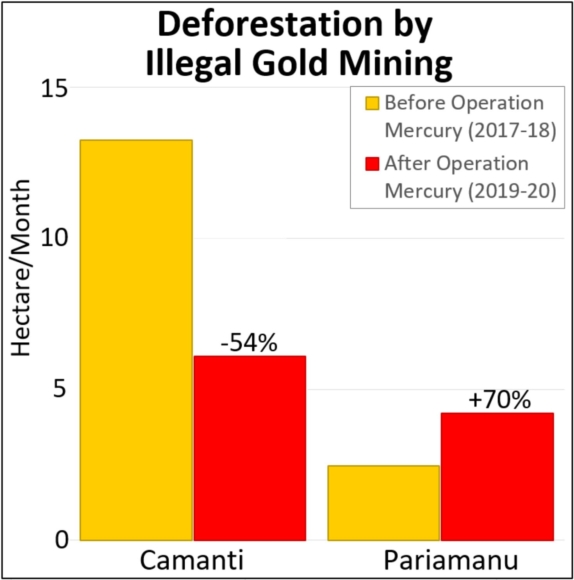
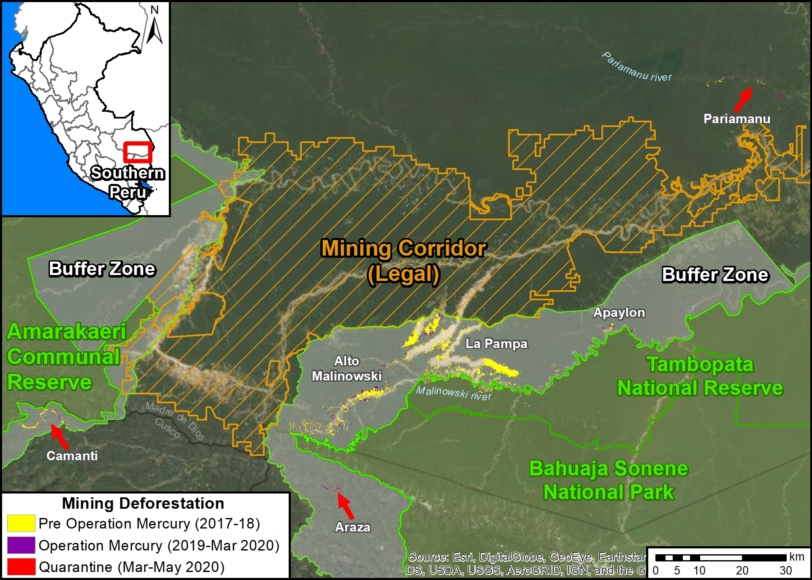
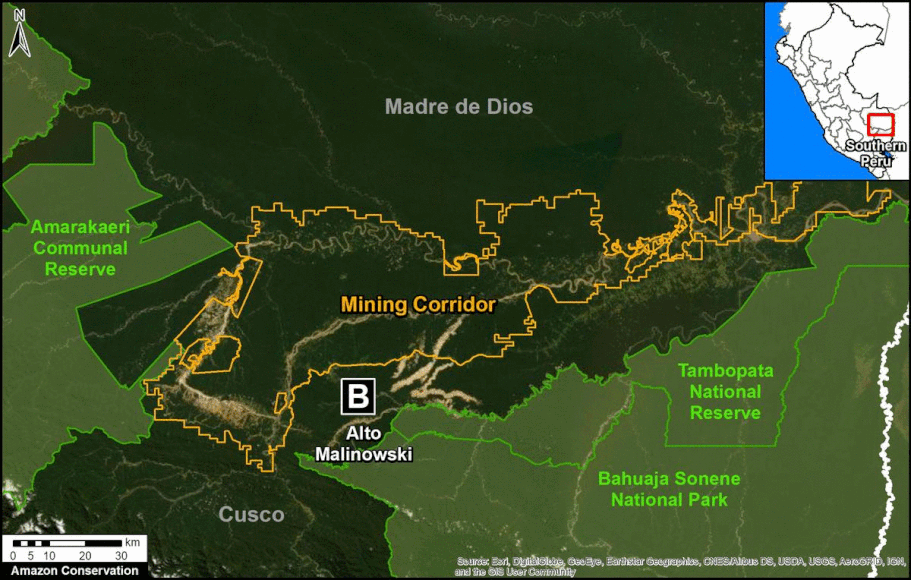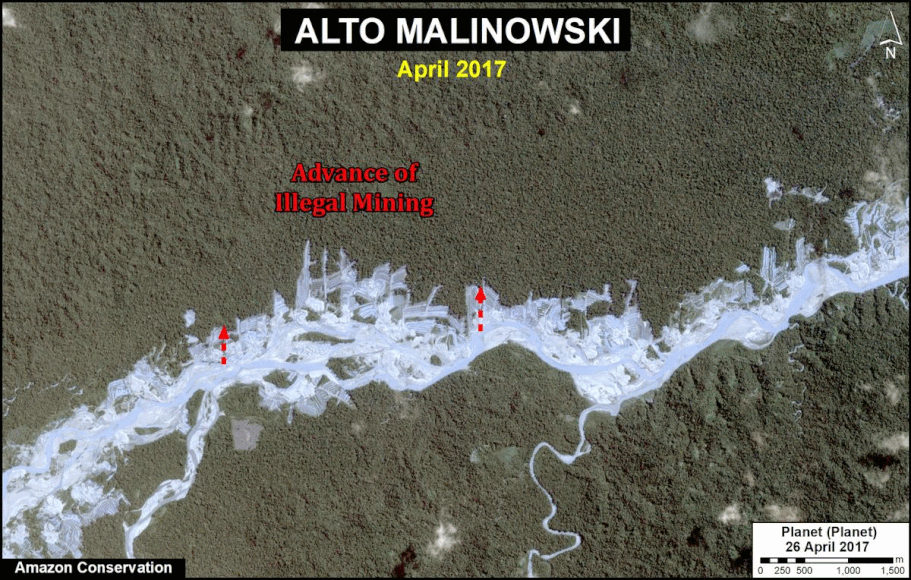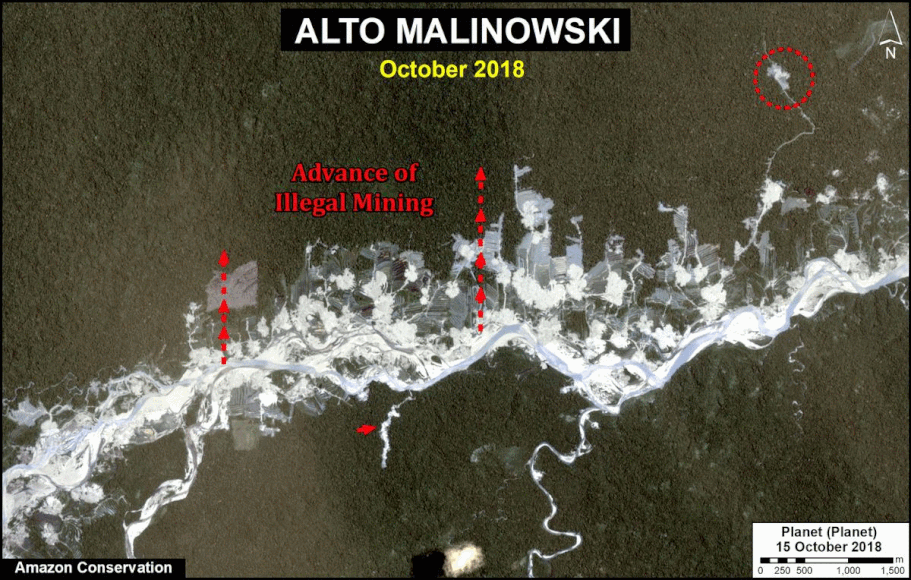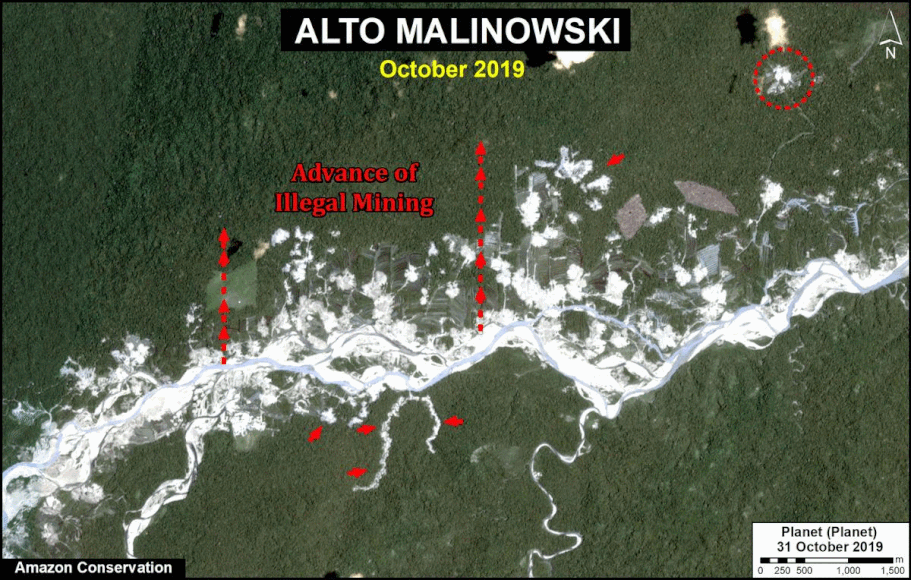
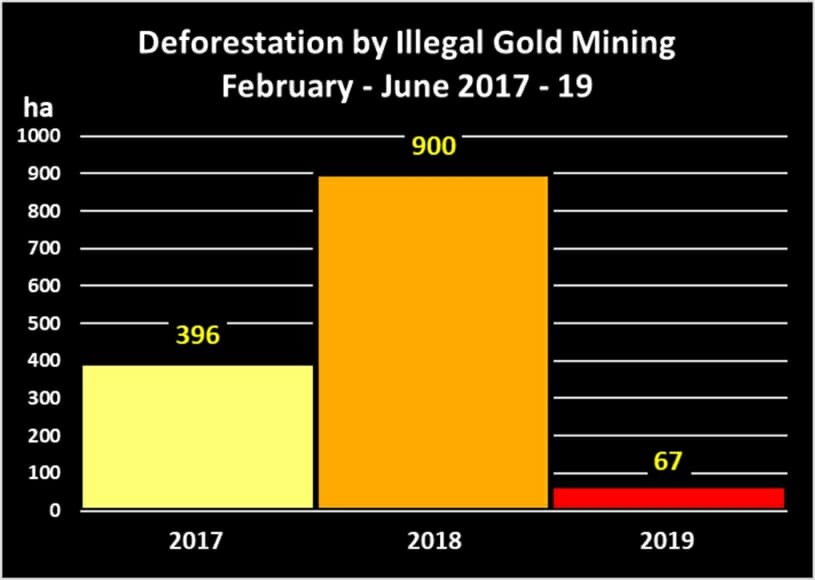
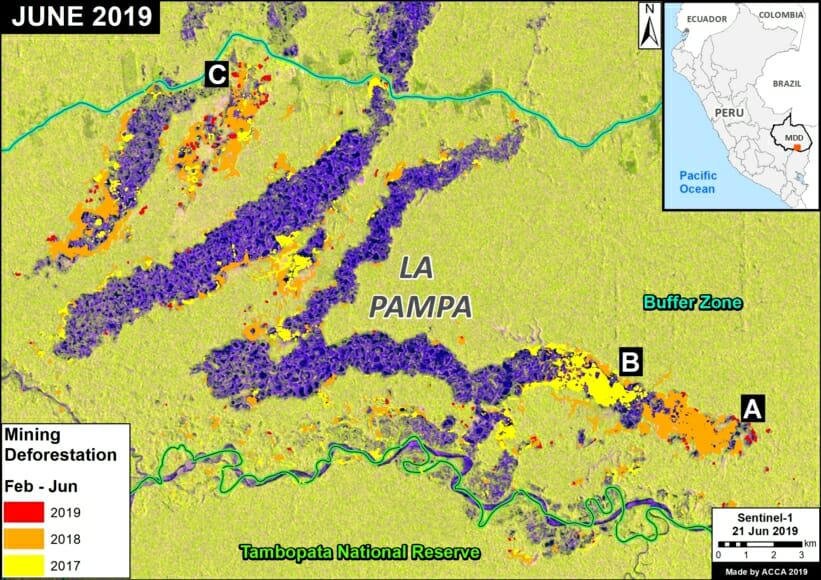
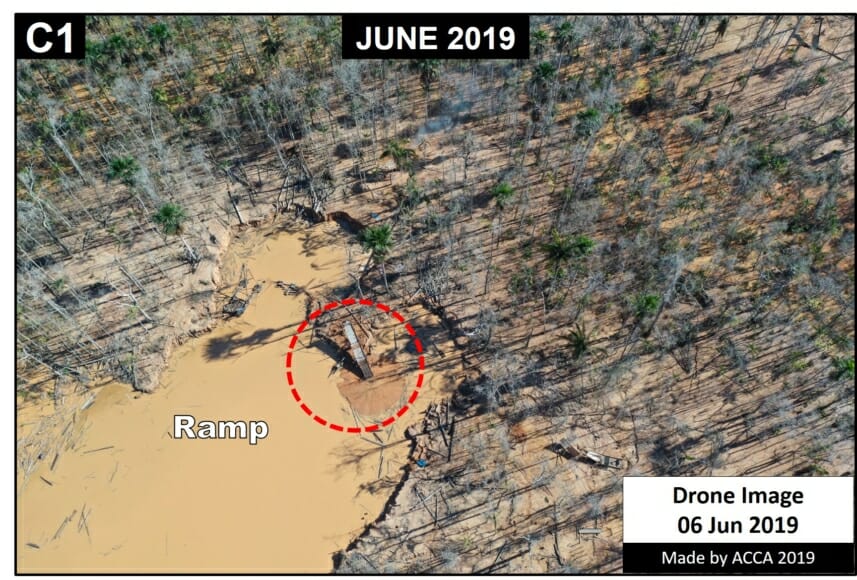
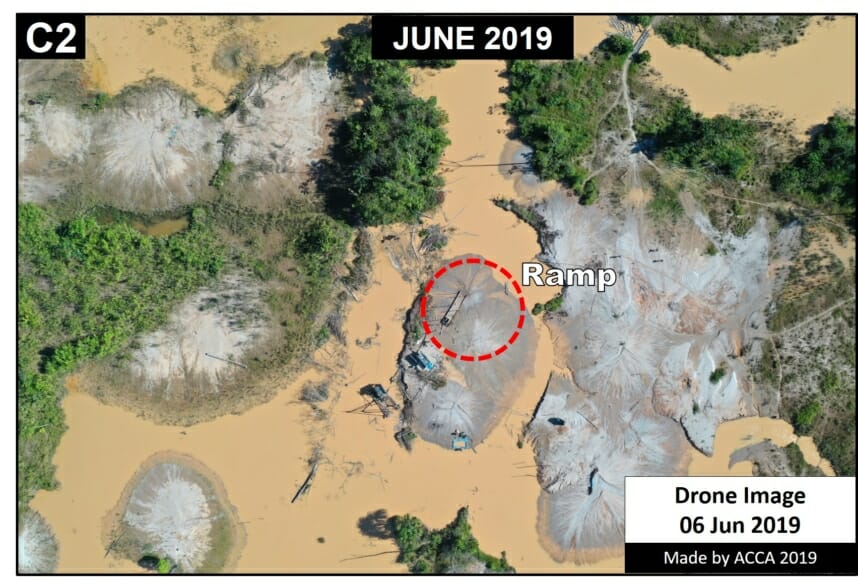
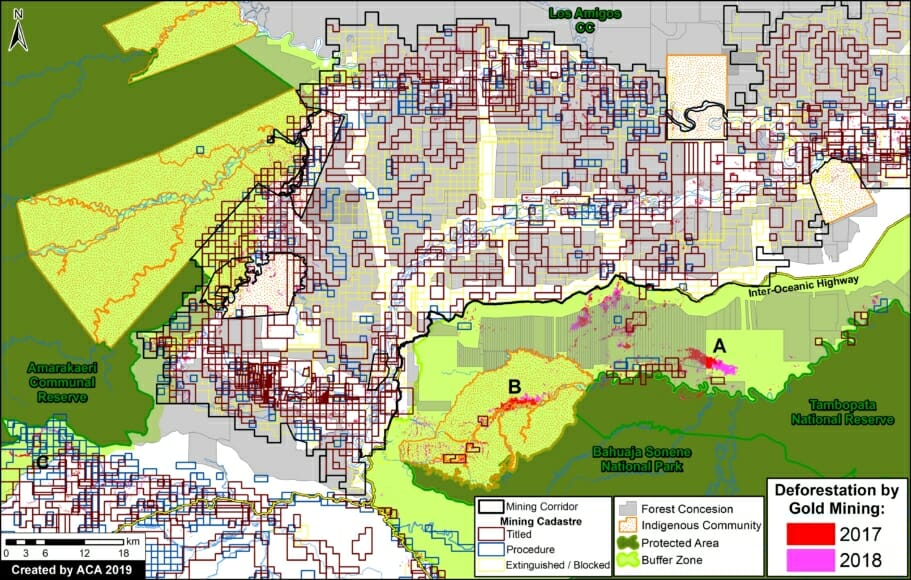
In MAAP #121, we reported that, in general, gold mining deforestation has decreased in the southern Peruvian Amazon following the government’s Operation Mercury, but it does continue in several critical areas. The images below show two of these areas (Pariamanu and Araza) with alarming new deforestation in 2020.
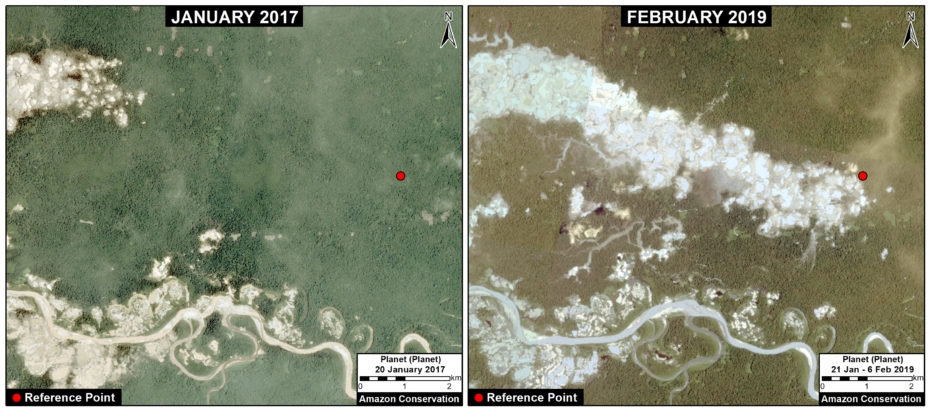
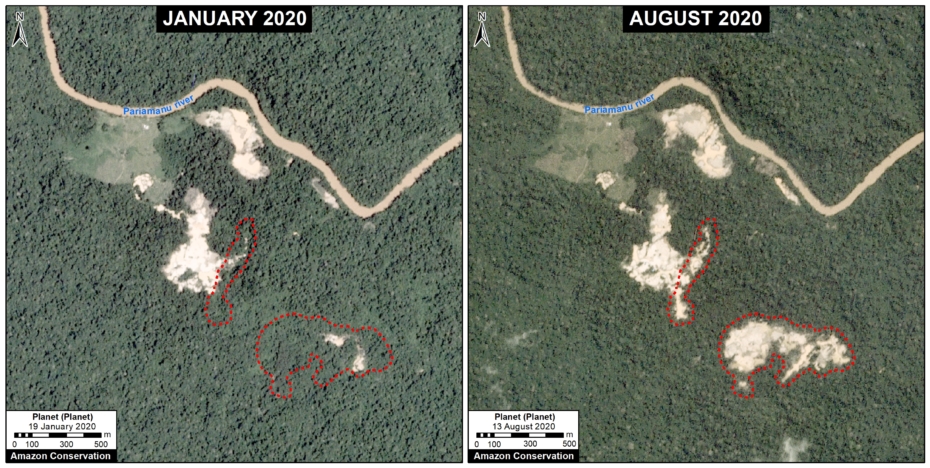
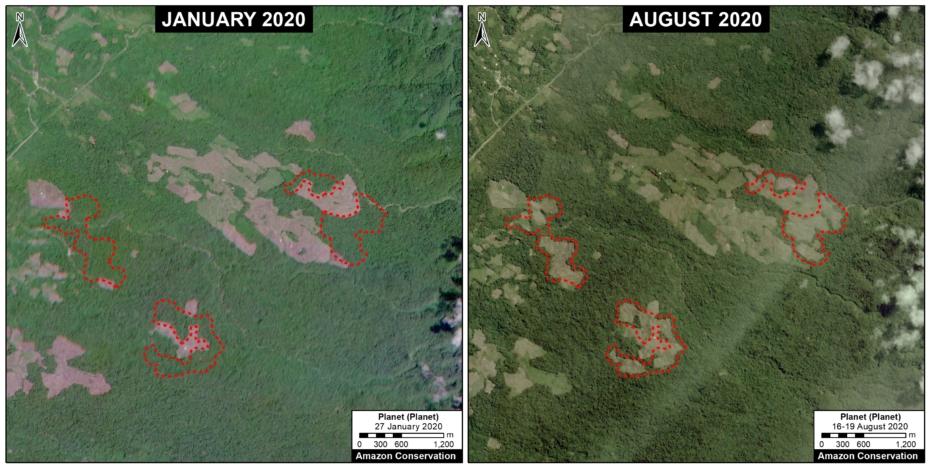
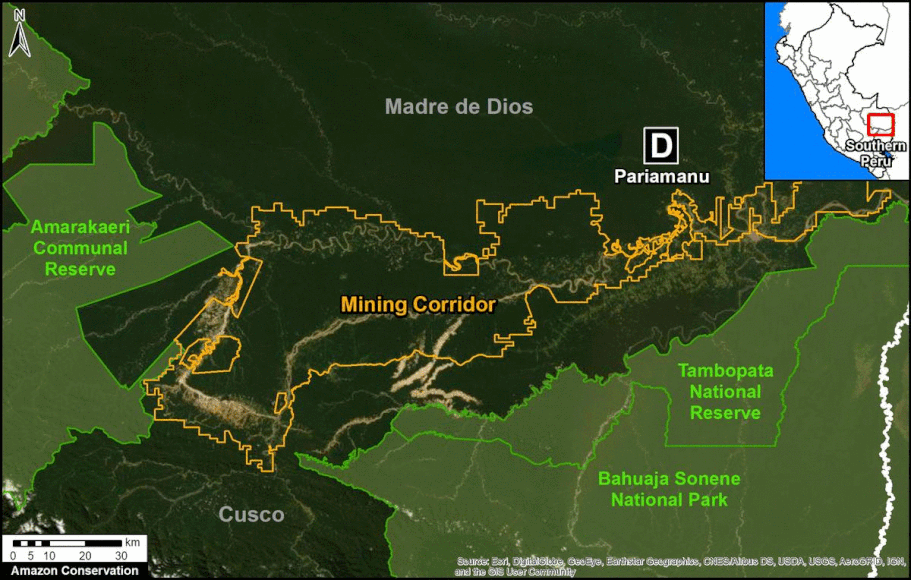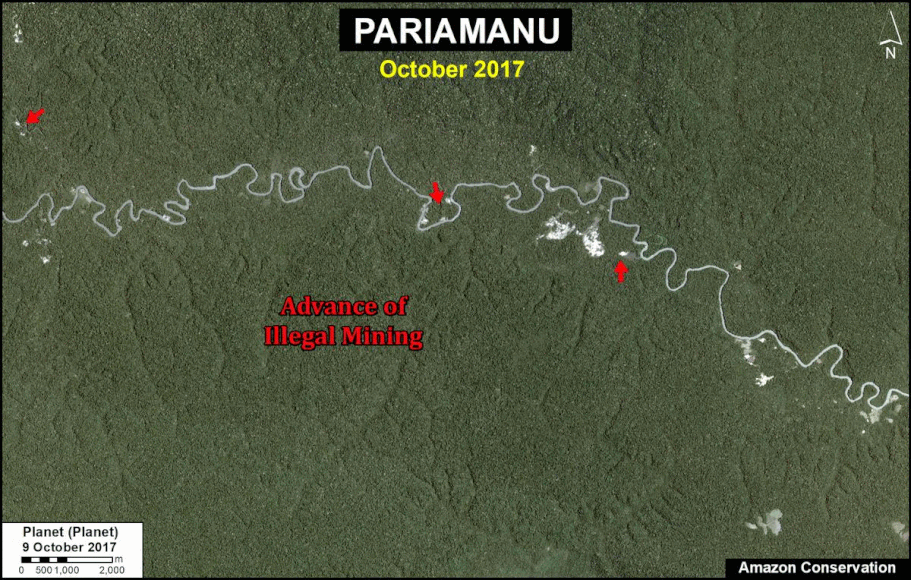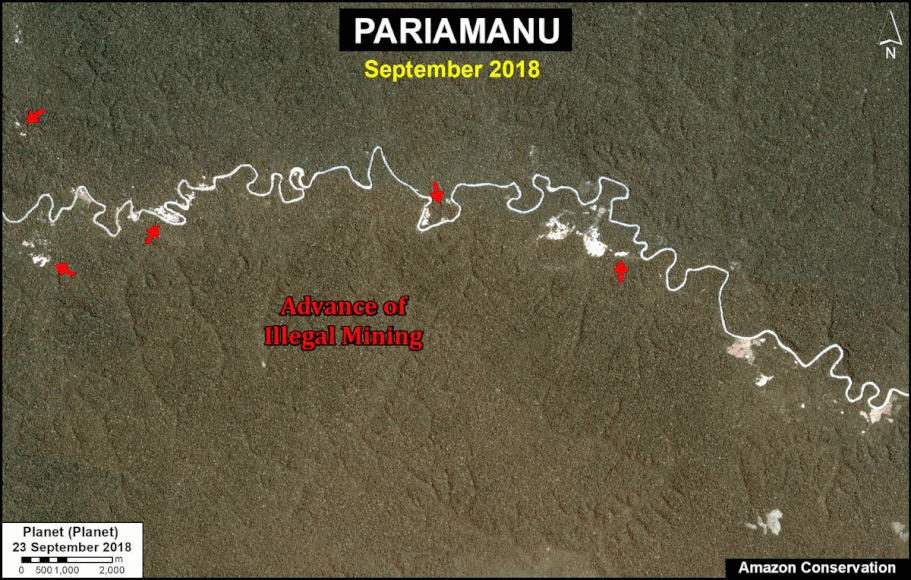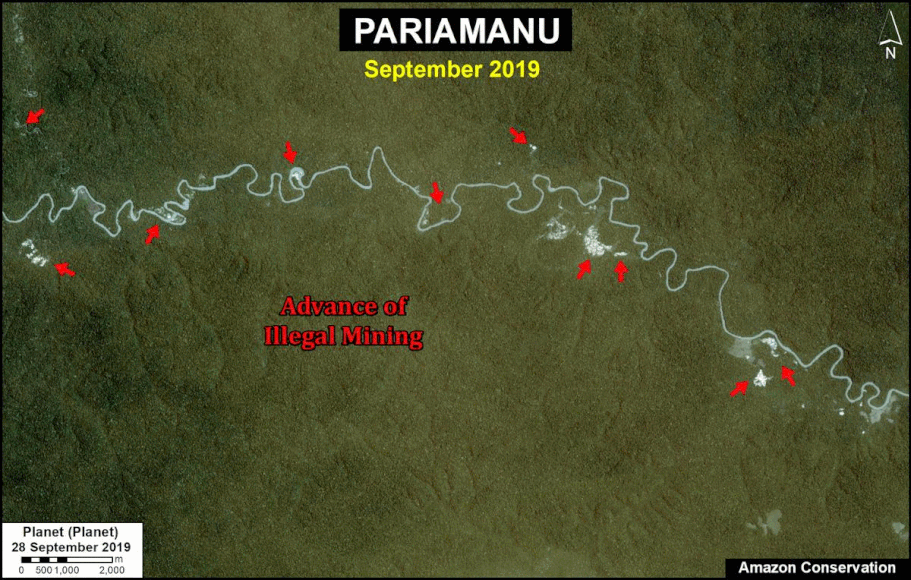
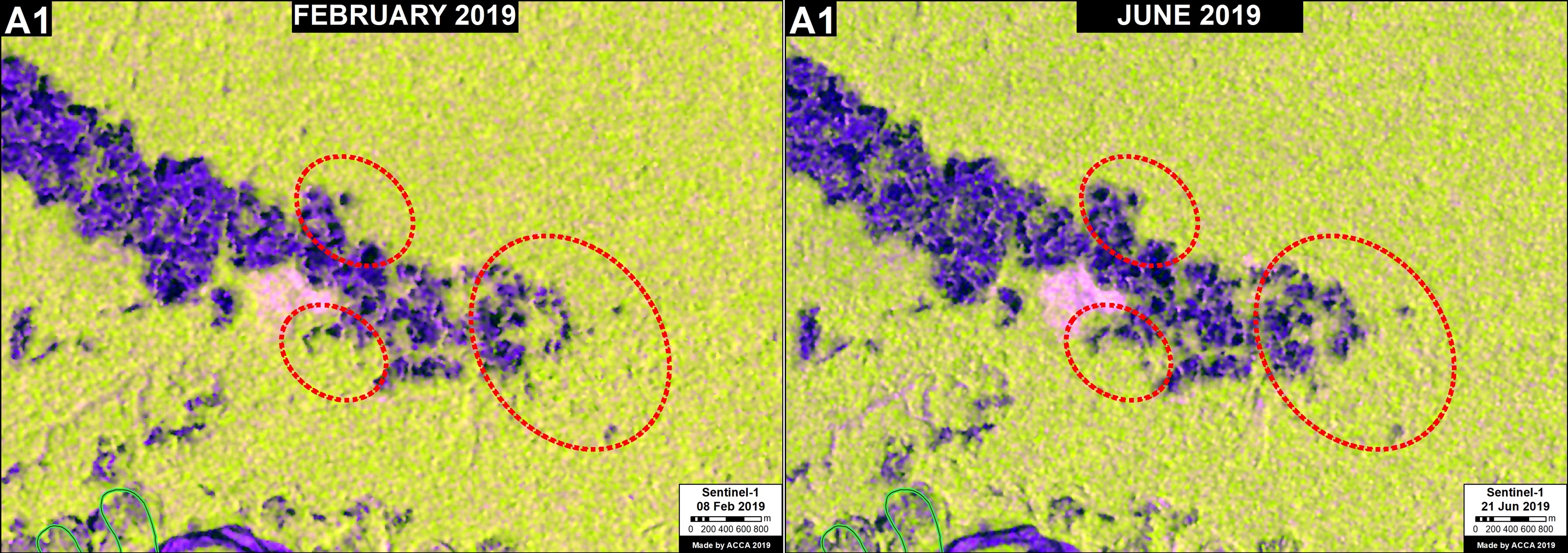
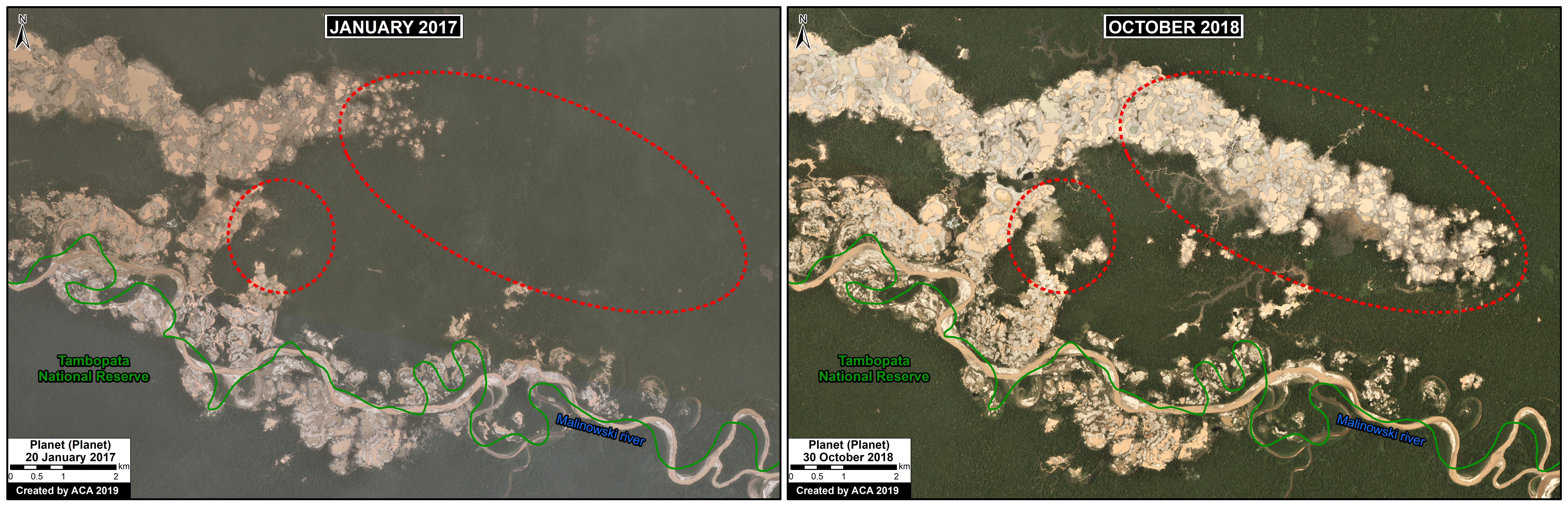
A. Pariamanu
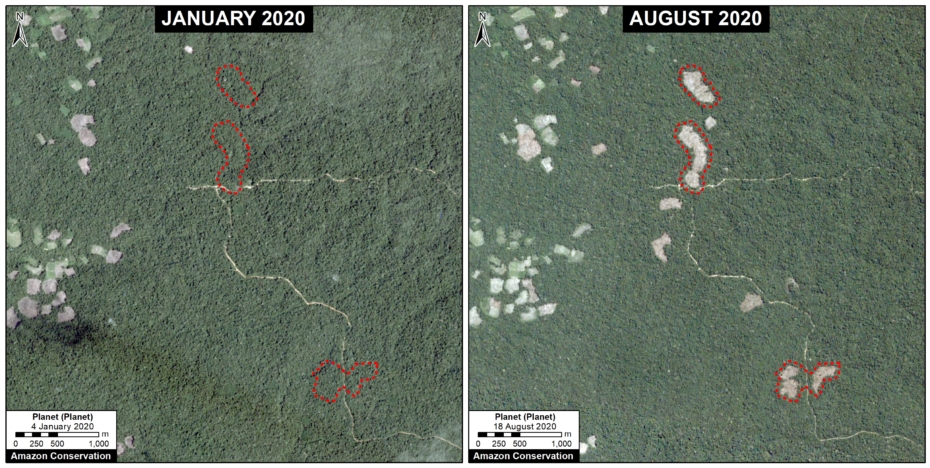
The following image shows the gold mining deforestation of 52 acres (21 hectares) of primary forest along the Pariamanu River in the southern Peruvian Amazon (Madre de Dios region) between January (left panel) and August (right panel) of 2020. We highlight that the Peruvian government has just carried out an operation against the illegal mining activity in this area.
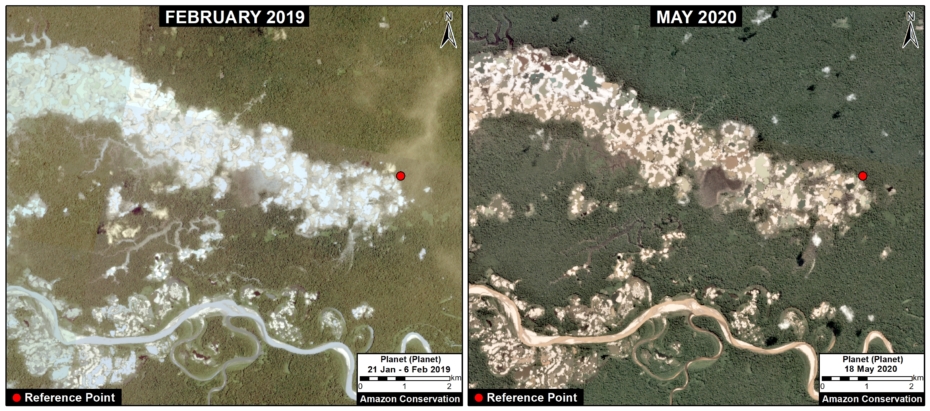
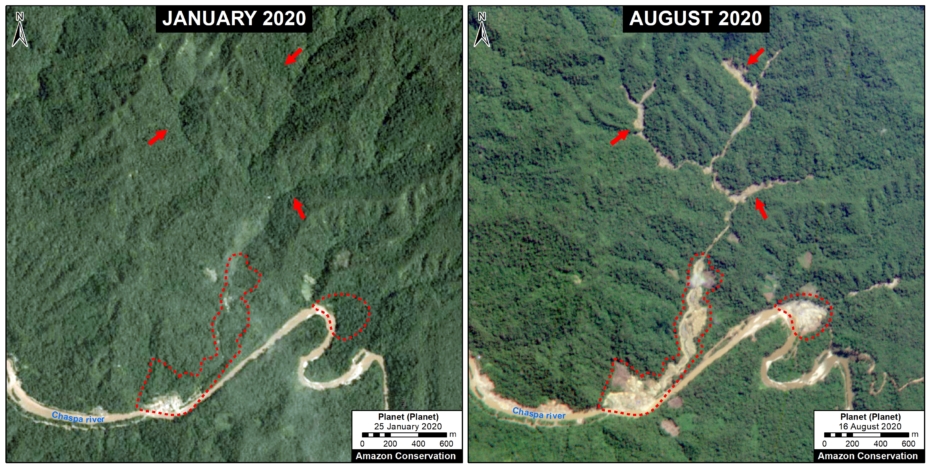
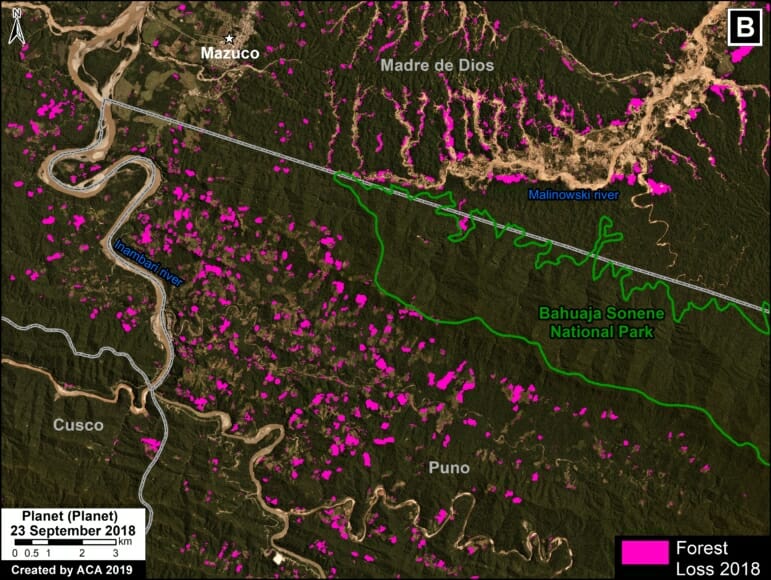
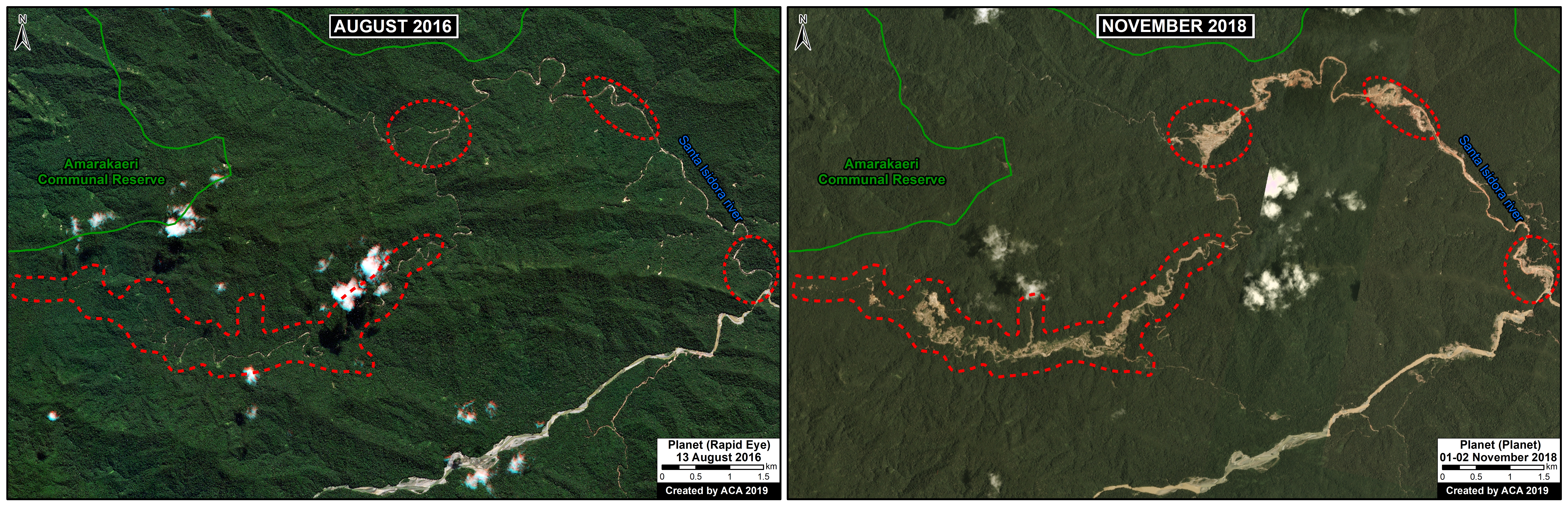
B. Araza
The following image shows the gold mining deforestation of 114 acres (46 hectares) along the Chaspa River in the Puno region, between January (left panel) and August (right panel) of 2020.
2. Large-scale Agriculture
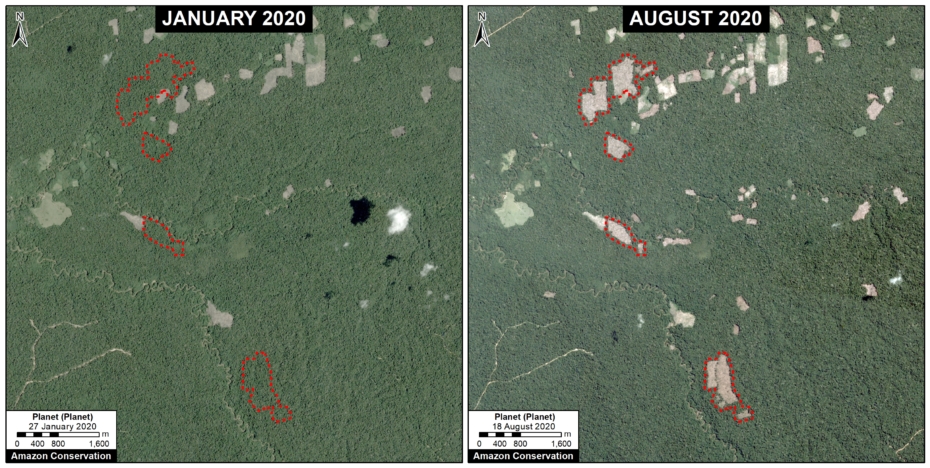
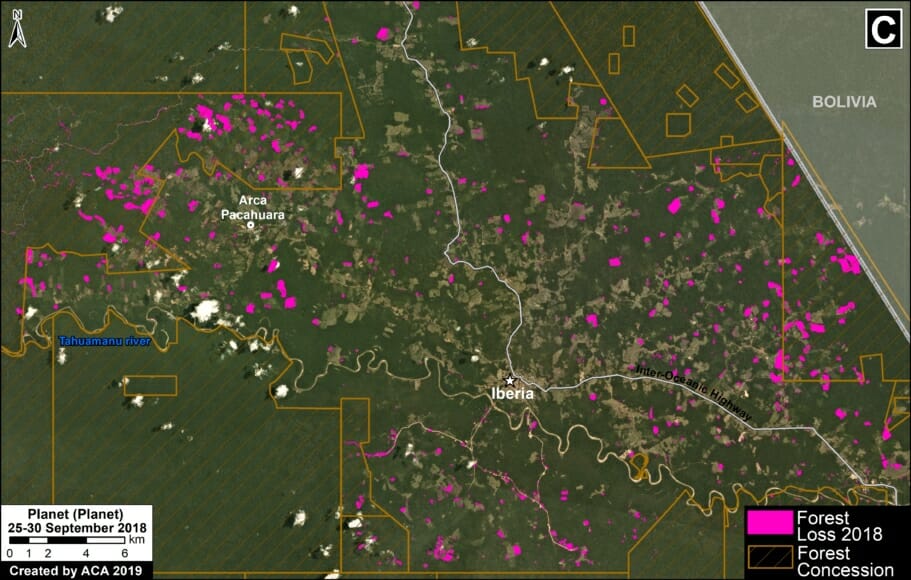
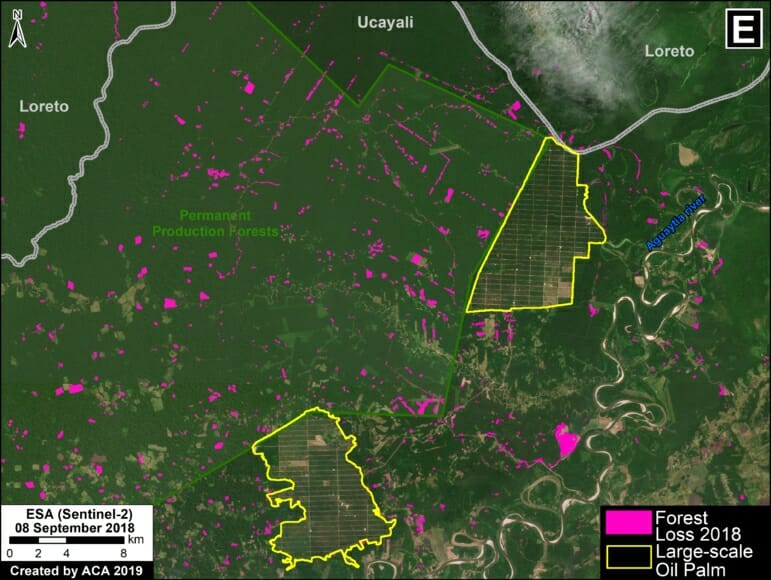
C. Mennonite Colony (near Tierra Blanca)
We reported last year that a new colony of Mennonites caused the deforestation of 4,200 acres (1,700 hectares) between 2017 and 2019 in the Loreto region (MAAP #112). The following image shows the additional deforestation of 820 acres (332 hectares) in 2020 between January (left panel) and August (right panel).
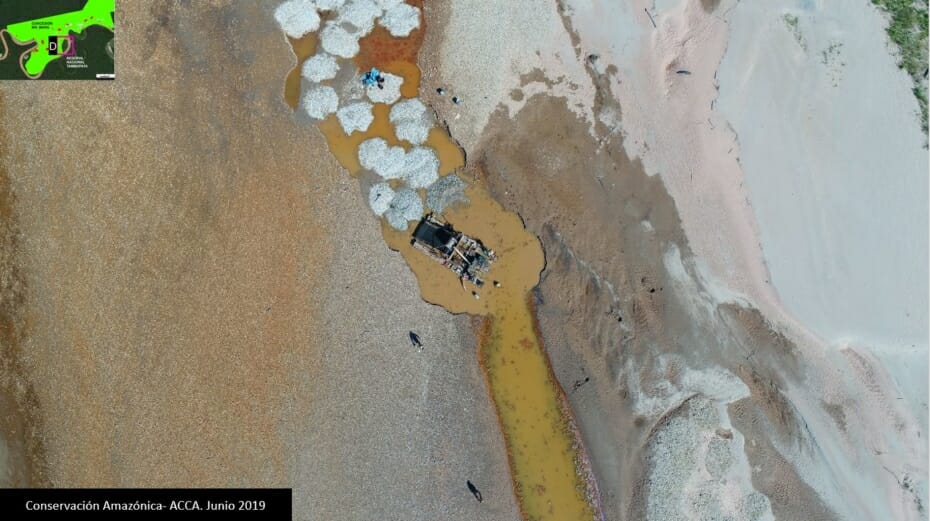
3. Small-scale Agriculture
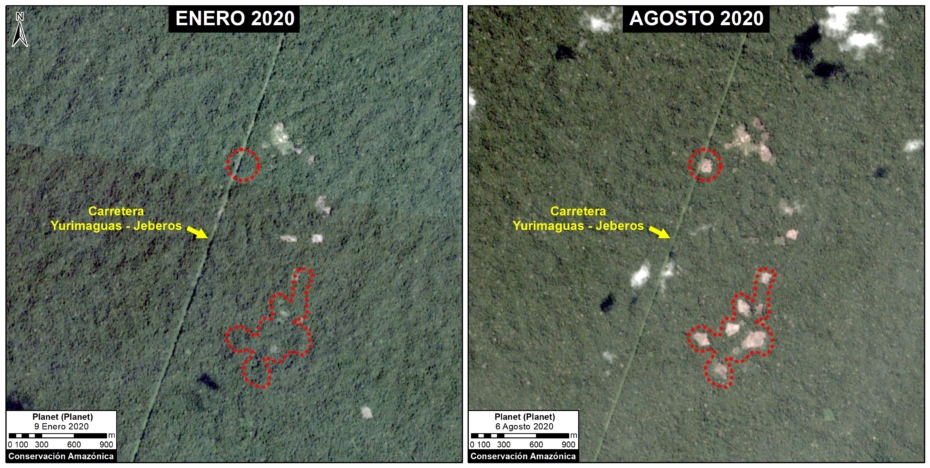
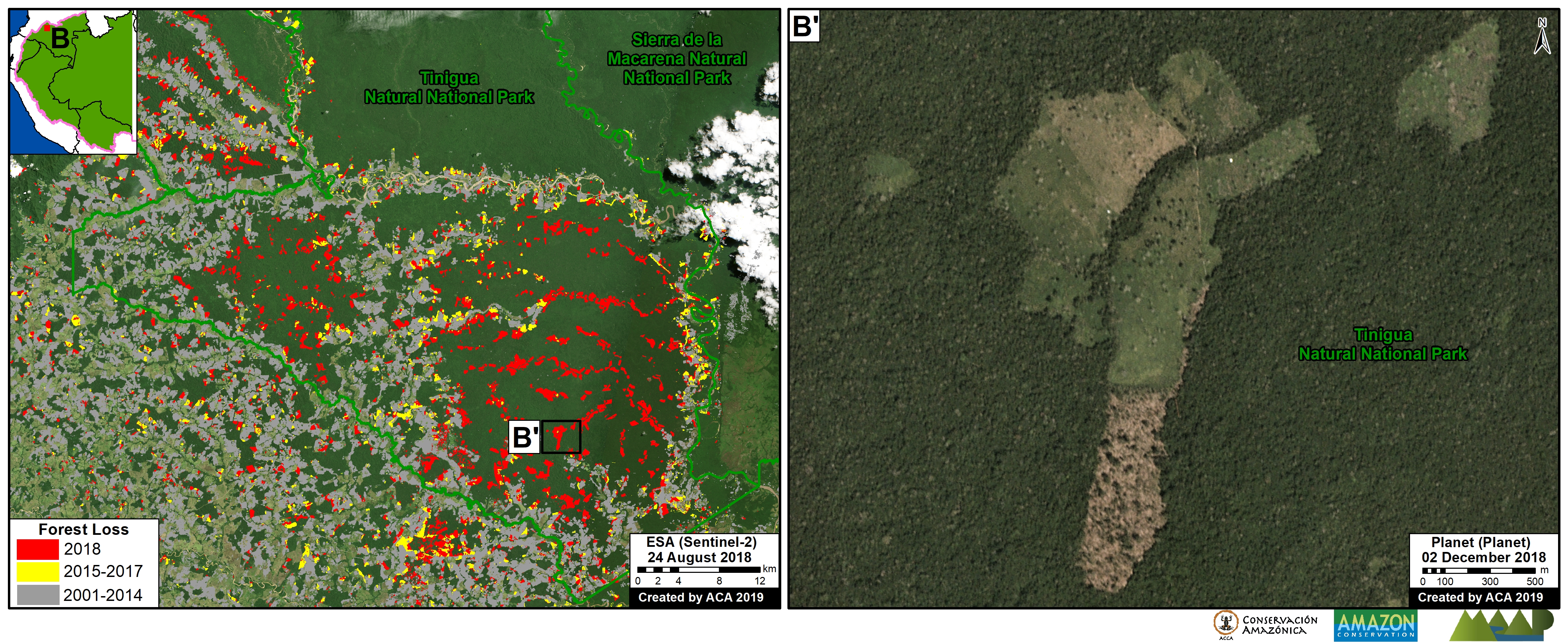
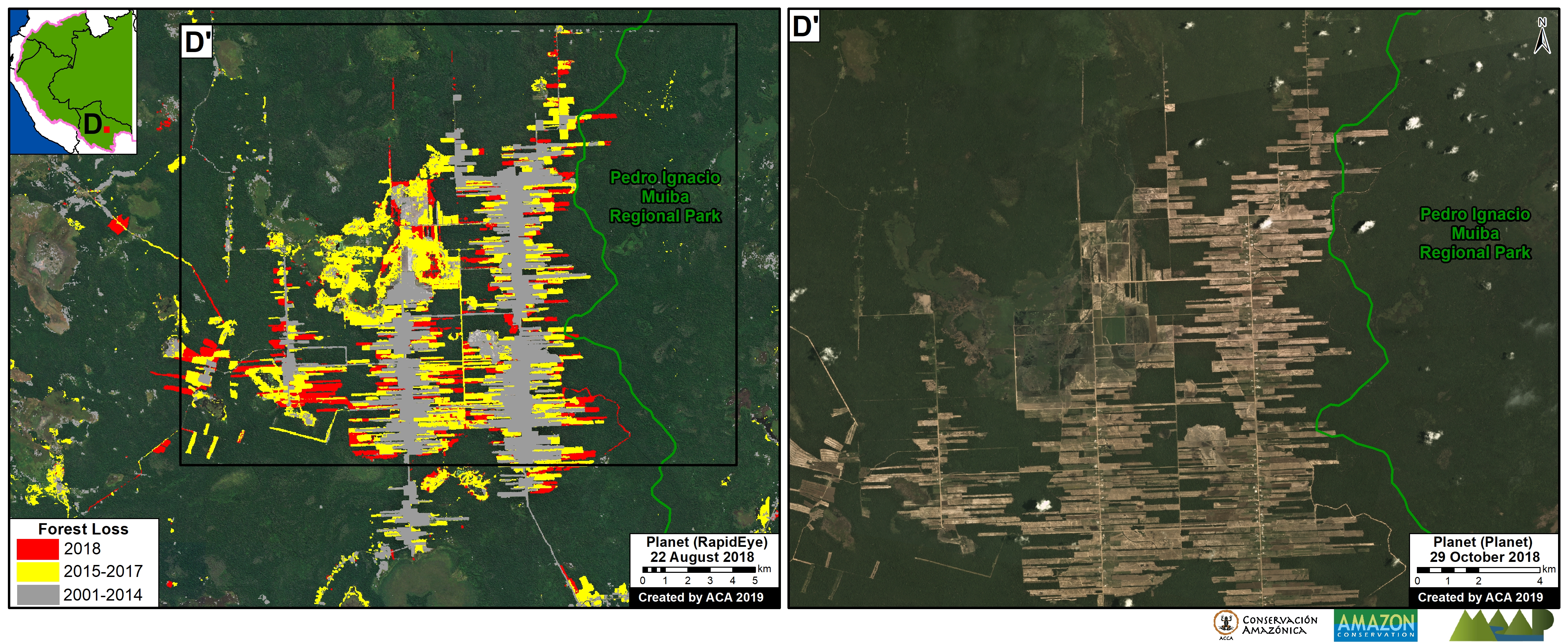
D. Jeberos
In 2018, we reported on the construction of a new road (65 km) cutting through primary forest in the Loreto region, between the city of Yurimaguas and the town of Jeberos (MAAP #84). The following image shows the deforestation of 40 acres (16 hectares) along the new road in 2020, between January (left panel) and August (right panel).
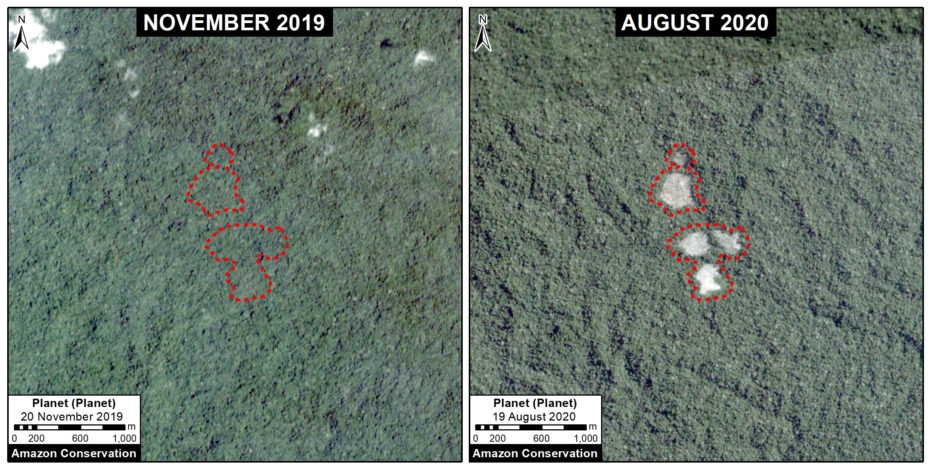
E. Las Piedras
The following image shows the deforestation of 64 acres (26 hectares) of primary forest in a Brazil-nut concession along the Las Piedras River in the Madre de Dios region, between November 2019 (left panel) and August 2020 (right panel) .
F. Bolognesi
The following image shows an example of deforestation (580 acres or 235 hectares) in one of the areas with the highest concentration of forest loss, located in the Ucayali region.
G. Santa Maria de Nieva
The following image shows an example of deforestation(346 acres or 140 hectares) in another one of the areas with the highest concentration of forest loss, located in the Amazonas region.
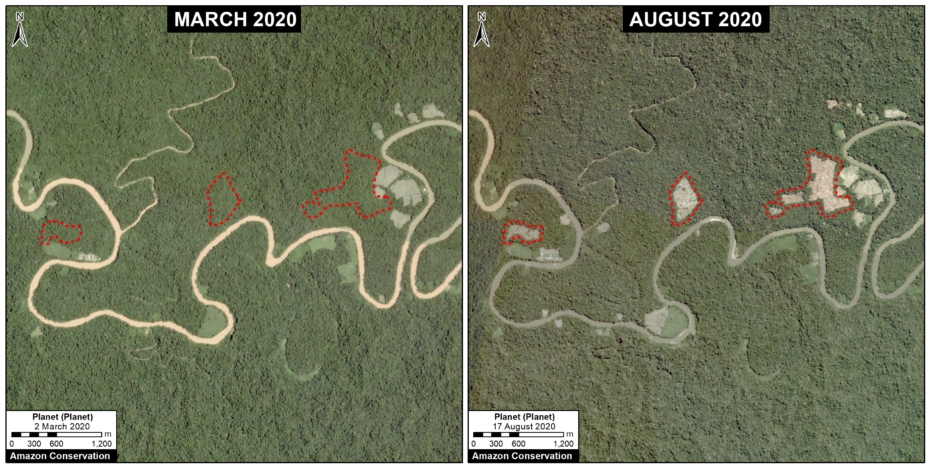
H. Mishahua River
The following image shows the recent deforestation of 168 acres (68 hectares) along the Mishahua River, in the Ucayali region. Just to the north, we documented extensive deforestation along the Sepahua River in 2019, where it also appears to be starting up again in 2020.
I. South of Sierra del Divisor National Park
The following image shows an example of deforestation (166 acres or 67 hectares) in another one of the areas with the highest concentration of forest loss, located south of the Sierra del Divisor National Park in the Ucayali region.
Metodology
The analysis was based on early warning GLAD alerts from the Universidad de Maryland and Global Forest Watch.
To identify the deforestation hotspots, we conducted a kernel density estimate. This type of analysis calculates the magnitude per unit area of a particular phenomenon, in this case forest cover loss. We conducted this analysis using the Kernel Density tool from Spatial Analyst Tool Box of ArcGIS. We used the following parameters:
Search Radius: 15000 layer units (meters)
Kernel Density Function: Quartic kernel function
Cell Size in the map: 200 x 200 meters (4 hectares)
Everything else was left to the default setting.
For the Base Map, we used the following concentration percentages: Medium: 7-10%; High: 11-20%; Very High: >20%.
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Novoa and G. Palacios for helpful comments to earlier versions of this report.
This work was supported by the following major funders: Erol Foundation, Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation (NORAD), and International Conservation Fund of Canada (ICFC).
Citation
Finer M, Mamani N (2020) Deforestation Hotspots 2020 in the Peruvian Amazon. MAAP: 124.